Hybrid Turbocharger for Marine Engines Market
Hybrid Turbocharger for Marine Engines Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Engine Layout (Single Turbo, Twin Turbo, Variable Geometry Turbo), By Operation (Diesel, Electric, Hybrid), By Application (Cargo Ships, High Speed Boats, Cruises, Naval Ships, Recreational Boats, Others), By Region, By Competition, 2018-2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
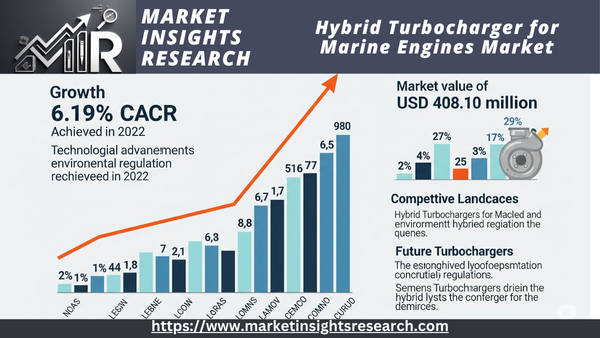
| Market Size (2022) | USD 408.10 million |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 6.19% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Cruises |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
Market Overview
The global hybrid turbocharger market for marine engines was valued at USD 408.10 million in 2022 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period, with a CAGR of 6.19% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
The hybrid turbocharger for marine engines market is the segment within the maritime industry dedicated to the development, production, distribution, and adoption of turbocharging systems specifically engineered for marine engines featuring a hybrid configuration. These advanced systems integrate conventional turbocharging technology with sophisticated electrical components and control systems to optimize the performance, efficiency, and environmental sustainability of marine propulsion systems.
Essentially, hybrid turbochargers are specialized devices designed to improve the operation of ship engines by efficiently managing air intake, optimizing combustion processes, and significantly reducing emissions. They achieve this through a combination of traditional exhaust-driven turbocharging and supplementary electrical power, which provides on-demand boost pressure and noticeably improves engine responsiveness.
The market for hybrid turbochargers in marine engines has gained significant traction due to the maritime industry's increasing emphasis on lowering emissions, enhancing fuel efficiency, and adhering to stringent environmental regulations. Consequently, manufacturers, shipbuilders, and vessel operators are actively exploring and investing in hybrid turbocharger technology to effectively address these challenges and achieve greener, more efficient marine transportation. This market represents a crucial component in the ongoing transformation of the maritime sector towards greater sustainability and enhanced operational performance.
Key Market Drivers
Stringent Emission Regulations
The maritime industry has witnessed a significant drive towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing air quality in recent years. This has resulted in the implementation of stringent emission regulations on a global scale. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set strict limits on sulfur emissions, and numerous countries have established Emission Control Areas (ECAs) with even more demanding requirements. To adhere to these regulations, ship operators are actively seeking innovative solutions, such as hybrid turbochargers, which can improve engine efficiency and lower emissions.
Hybrid turbochargers are instrumental in achieving compliance with these emission standards by optimizing engine performance. They enable engines to operate with greater efficiency, leading to more complete fuel combustion and a reduction in the release of harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter. Consequently, shipowners are increasingly investing in hybrid turbocharger technology not only to meet regulatory requirements and avoid potential penalties but also to contribute to a more environmentally friendly maritime industry.
Fuel Efficiency and Cost Savings
The desire for increased fuel efficiency and cost savings is another important factor propelling the marine engine market's adoption of hybrid turbochargers. Any technology that can lower fuel usage is widely desired by shipowners, as fuel expenses represent a significant operational expenditure.
Through improved air intake and combustion, hybrid turbochargers increase engine efficiency. They improve fuel combustion and reduce fuel usage by precisely supplying the engine with air. Over a vessel's operational lifetime, this results in significant cost savings. Hybrid turbochargers are becoming a more attractive option as ship operators search for methods to lower operating costs and maintain their competitiveness.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Increasing Demand for Power and Performance
Ships with more power and performance capabilities are becoming more and more in demand in the worldwide marine industry. The need to move heavier loads more rapidly and effectively is one of the many reasons for this demand. Ship owners and builders are therefore searching for technology that can increase engine power without sacrificing pollution or fuel efficiency.
A solution is provided by hybrid turbochargers, which enhance engine performance. Higher boost pressure levels from them allow marine engines to produce more power without appreciably raising pollution or fuel consumption. For vessels engaged in operations like container shipping, where power and speed are critical for fulfilling strict deadlines, this capacity is especially important.
Technological Advancements
The market for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines has been significantly influenced by developments in turbocharger technology. Turbochargers with increased features and capabilities are constantly being developed by manufacturers. Shipowners and operators that are eager to stay on the cutting edge of technology in order to obtain a competitive edge are taking notice of these developments.
Hybrid turbochargers are now more dependable and efficient than ever because to advanced control systems, new materials, and better designs. They are a flexible option for the maritime sector since they are also growing more tolerant of different engine sizes and kinds. Future maritime propulsion systems are anticipated to heavily rely on hybrid turbochargers as technology advances.
Environmental Awareness and Corporate Social Responsibility
The maritime sector has seen a dramatic change in recent years toward corporate social responsibility (CSR) and environmental awareness. To show their dedication to sustainability and lessen their environmental impact, many shipowners and operators are taking proactive steps. The adoption of technologies that can lessen emissions and the environmental impact of maritime activities is being fueled by this change.
Hybrid turbochargers support the industry's sustainability objectives by increasing engine efficiency and lowering emissions. Ships with hybrid turbochargers are a more environmentally friendly option because they release fewer pollutants into the atmosphere. A company's CSR profile is also improved by implementing such technology, which can benefit its reputation and business prospects.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Governments throughout the world are offering incentives and subsidies to promote the adoption of greener technologies, such as hybrid turbochargers, since they recognize how important it is to reduce emissions from the maritime industry. These incentives for installing eco-friendly equipment on older vessels can be in the form of grants, tax breaks, or subsidies.
A growing number of shipowners and operators are investing in hybrid turbochargers and other emission-reducing technologies by taking advantage of these financial incentives. The maritime industry finds cleaner technology more appealing because of these government programs, which not only encourage their adoption but also assist in defraying the initial investment expenses.
In conclusion, strict emission regulations, the desire for cost and fuel savings, the growing need for power and performance, technological advancements, environmental consciousness, and government incentives are all driving the global market for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines. In order to increase efficiency, lower emissions, and secure a sustainable future for the maritime industry, these factors work together to propel the development and uptake of hybrid turbocharger technology.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government Policies are Likely to Propel the Market
Emission Reduction Mandates and Regulations
The adoption of pollution reduction laws and regulations is one of the most important government initiatives propelling the global market for hybrid marine engine turbochargers. Concern over the effects of maritime traffic on the environment, especially with regard to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, is growing among governments worldwide.
Regulators like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) have established stringent emission reduction goals and rules in response to these worries. Annex VI of the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) establishes strict guidelines for lowering nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and restricts the amount of sulfur in marine fuels. In order to ensure compliance with international standards, these laws encourage shipowners and operators to implement technologies such as hybrid turbochargers to improve engine efficiency and lower emissions.
In addition to safeguarding the environment, governments are encouraging the market expansion of hybrid turbochargers as a necessary option to satisfy these strict regulations by implementing these emission reduction criteria.
Subsidies and Financial Incentives
Many governments throughout the world are actively encouraging the use of clean technologies through financial incentives and subsidies because they understand how important it is to reduce emissions from the maritime sector. These incentives can be in the form of grants, tax breaks, or research and development subsidies, among other things.
For instance, shipowners that purchase hybrid turbochargers and other emission-reducing equipment may be eligible for tax incentives from certain governments. Subsidies for research and development also promote the creation of more sophisticated hybrid turbocharger technologies that further lower emissions and boost fuel economy.
By making hybrid turbocharger technology more financially feasible and hastening its adoption in the maritime sector, these financial incentives are essential in motivating shipowners and operators to make the investment.
Fuel Efficiency Standards
Government and regulatory bodies' fuel economy requirements have an effect on the marine engine hybrid turbocharger market. These regulations are set by governments in an effort to lower ship fuel usage and, consequently, greenhouse gas emissions.
Shipowners can assist their boats achieve or above these regulations by improving their fuel efficiency through the installation of hybrid turbochargers. In addition to lowering operating expenses, this supports government efforts to lessen the marine industry's negative environmental effects.
In order to create and update fuel economy standards, government organizations frequently interact with industry partners. This ensures that technological improvements, such as hybrid turbochargers, are taken into account in the regulatory framework.
Research and Development Funding
The market for hybrid turbochargers is greatly impacted by government regulations that encourage research and development (R&D) activities in the maritime sector. Numerous governments set aside money to promote the creation of cutting-edge, environmentally friendly marine engine technologies.
Manufacturers and engineering companies can invest in the development and testing of hybrid turbochargers and related technologies thanks to this R&D financing. It encourages the development of hybrid turbochargers that are more dependable and efficient, enabling them to satisfy the changing demands of the marine sector.
Governments may promote the development of hybrid turbocharger technology and its broad use in the worldwide maritime industry by funding research and development.
Port Emission Reduction Initiatives
Governments frequently enact laws intended to lower emissions from port operations in addition to regulating emissions from vessels. Improved cargo handling equipment, shore power facilities, and laws mandating that ships convert to greener fuels while in port are some examples of these projects.
Hybrid turbochargers complement these port pollution reduction programs by increasing vessel efficiency and lowering emissions. Ships with hybrid turbochargers can lower their emissions while at port as well as while traveling.
Governments may provide incentives or infrastructure assistance for ships that use hybrid turbocharger technology in order to promote compliance with these programs and accelerate the adoption of this technology.
International Collaboration and Agreements
Because sea transportation is an international activity, nations must work together and reach agreements to manage environmental issues. In order to establish uniform criteria for emissions, fuel quality, and technological adoption, governments frequently take part in international accords.
The Ballast Water Management Convention, for instance, attempts to stop the spread of dangerous aquatic species by limiting the flow of ballast water. In order to comply with the standards set forth in these accords, governments that have ratified these conventions encourage the employment of environmentally friendly technologies, such as hybrid turbochargers.
Governments can guarantee regional harmonization of legislation and regulations through international cooperation, thereby establishing a fair playing field for the use of hybrid turbocharger technology in the global maritime industry.
In conclusion, the global market for hybrid marine engine turbochargers is greatly influenced by government regulations. Hybrid turbocharger technology acceptance is greatly aided by regulations requiring pollution reductions, financial incentives, fuel efficiency standards, research and development funding, port emission reduction programs, and international cooperation. In addition to helping the environment, these regulations stimulate economic expansion and innovation in the marine sector, which eventually makes it more efficient and sustainable.
Key Market Challenges
Initial Investment Costs and Return on Investment
The comparatively high upfront costs of implementing this technology are one of the main obstacles facing the global market for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines. Some shipowners and operators may find the initial expenses of hybrid turbochargers prohibitive, despite the fact that they provide significant long-term advantages in terms of increased engine efficiency, lower emissions, and fuel savings.
It usually takes a lot of engineering effort, adjustments to the current engine systems, and the acquisition of specialist equipment to install a hybrid turbocharger. The retrofitting procedure may also involve downtime, which could affect a vessel's working schedule and ability to generate income.
Many shipowners may find the initial investment to be a turnoff, particularly those with limited funds or those operating older vessels. Without a clear grasp of the ROI and the timeframe for recovering their investment, they could be reluctant to make such a large financial commitment.
Manufacturers of hybrid turbochargers and other industry participants must cooperate to create affordable solutions and financing alternatives in order to overcome this obstacle. By providing subsidies or incentives to defray the initial investment expenses, governments can also help make hybrid turbochargers more affordable for a wider variety of vessel operators.
Furthermore, the industry ought to offer shipowners thorough ROI analyses that illustrate the long-term financial advantages of implementing hybrid turbochargers, such as decreased fuel usage, fewer maintenance expenses, and adherence to emission standards. Shipowners may make well-informed judgments about investing in this technology with the aid of transparent and easy-to-understand ROI calculations.
Integration and Compatibility Issues
The difficulty of combining hybrid turbocharger systems with current engine layouts is another major obstacle facing the global market for marine engines. varying engine types, which might differ in size, power output, and design, are used in ships of varying sizes. It might be somewhat difficult to guarantee smooth compatibility and integration with these various engine systems.
For hybrid turbocharger systems to meet the unique requirements and features of a vessel's engine, careful engineering and modification are needed. Performance inefficiencies, higher maintenance needs, and even mechanical failures can result from incompatibilities. Because older boats may have antiquated engine systems that were not initially built with hybrid technology in mind, these difficulties can be more troublesome when retrofitting them with hybrid turbochargers.
The industry needs to focus its research and development efforts on developing flexible and standardized hybrid turbocharger solutions in order to address these integration and compatibility issues. To create hybrid turbochargers that can be easily incorporated into a variety of engine configurations, producers ought to collaborate closely with shipbuilders and engine manufacturers.
The industry should also make investments in cutting-edge software and control systems that can maximize hybrid turbocharger performance and guarantee engine compatibility. This could entail creating intuitive user interfaces that let ship engineers keep an eye on and modify hybrid turbocharger settings for peak performance.
To reduce the possibility of compatibility problems, industry participants should also set precise rules and best practices for the integration and installation of hybrid turbochargers. To successfully handle these issues and guarantee that hybrid turbochargers can be easily implemented throughout the marine industry, cooperation between manufacturers, shipowners, and regulatory agencies is essential.
In conclusion, the global market for marine engine hybrid turbochargers faces difficulties with integration and compatibility with various engine systems, as well as initial investment costs and return on investment considerations. Manufacturers, shipowners, governments, and industry associations must work together to address these issues and create affordable solutions, funding alternatives, and standardized integration procedures. To fully utilize hybrid turbocharger technology in enhancing the sustainability and efficiency of maritime transportation, these obstacles must be overcome.
Segmental Insights
Engine Layout Insights
In 2022, the market share that was largest was held by the Single Turbo sector. Single turbochargers are renowned for being easy to use and reasonably priced. Compared to more intricate configurations like dual turbochargers or variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs), they often require less maintenance and installation because they have fewer parts. Smaller ships or those with less maintenance resources may find this simplicity appealing. Smaller marine engines with lower power requirements frequently use single turbochargers. One turbocharger might be enough to give enough boost for ships with engines in this size range without the need for more intricate systems. Larger VGT systems or multiple turbochargers can be difficult to install on some ships due to their small engine rooms. A single turbocharger might be the most sensible option in these situations. Some marine engines are built to function best with just one turbocharger. Using a single turbocharger may be in line with the unique turbocharging setups that engine manufacturers have in mind when designing their engines. One important factor to take into account is the expense of adding hybrid turbochargers to an existing vessel. For vessel owners, single turbochargers might be a more economical choice, especially when taking installation and early investment expenses into account.
Application Insights
In 2022, the biggest market share was held by the Cargo Ships segment. Because of their lengthy journeys and massive engines, cargo ships are notorious for using a lot of gasoline. Cargo ship owners have been under pressure to lower emissions, especially sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and greenhouse gases, as the marine sector is subject to stricter environmental rules. Hybrid turbochargers are essential for improving emissions and fuel economy. These turbochargers reduce fuel usage and enable cargo ships fulfill emissions regulations by improving combustion and air intake. Cargo ships have strict budgets and timetables. A significant amount of their operating expenditures are related to fuel. Over time, hybrid turbochargers provide significant cost savings by increasing fuel efficiency. For cargo ship owners and operators, hybrid turbochargers are an alluring investment since they use less fuel, which results in lower operating costs. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) and other international emissions restrictions apply to cargo ships that travel on international routes. For example, the IMO's MARPOL Annex VI places stringent restrictions on sulfur emissions and mandates that cleaner fuels or emission-reducing devices, such as hybrid turbochargers, be used in emission control areas (ECAs). For cargo ships to stay out of trouble and continue operating internationally, compliance with these rules is essential. Depending on the size and purpose of the ship, cargo ships can have highly tailored engines, making them some of the largest vessels in the marine sector. This adaptability enables cargo ship operators to improve engine performance and emissions control by choosing the best turbocharger configuration, be it a single turbocharger, twin turbochargers, or variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs). Operators of cargo ships are realizing more and more how important sustainability and environmental responsibility are. Their attempts to lessen the environmental effect of their operations are in line with the adoption of technology like hybrid turbochargers, which can improve their company's reputation and image in a world where environmental consciousness is growing.
Regional Insights
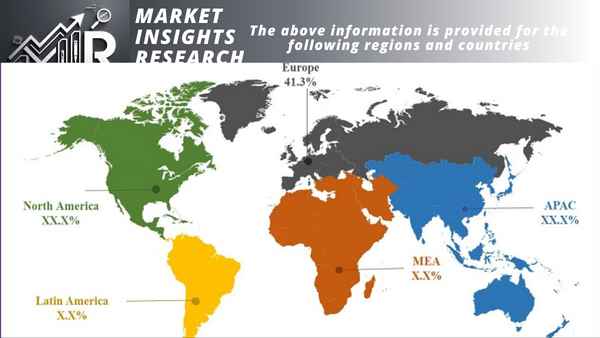
North America
The North American market for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines is expected to grow at a steady pace during the forecast period. The region is home to a number of major shipping companies and shipbuilders. The growing demand for marine engines from the region is expected to drive the growth of the hybrid turbocharger market in North America.
Europe
The European market for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines is expected to be the largest market during the forecast period. The region has a strong shipbuilding industry and is home to a number of major shipping companies. The stringent emission regulations in the region are expected to drive the demand for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific market for hybrid turbochargers for marine engines is expected to be the fastest-growing market during the forecast period. The region is home to a number of major shipping companies and shipbuilders. The growing demand for marine engines from the region is expected to drive the growth of the hybrid turbocharger market in the Asia Pacific region.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In March 2023, BorgWarner announced that it would invest USD100 million in its hybrid turbocharger manufacturing facility in Augsburg, Germany. The investment is expected to create 200 new jobs and increase the production capacity of the facility by 50%.
- In April 2023, Garrett Motion announced that it would partner with China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC) to develop and produce hybrid turbochargers for marine engines. The partnership is expected to accelerate the commercialization of hybrid turbochargers in the Chinese marine market.
- In May 2023, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) announced that it had developed a new hybrid turbocharger for marine engines that is expected to improve fuel efficiency by up to 10%. The new turbocharger is scheduled to be released in 2024.
- In June 2023, Napier Turbochargers announced that it had raised USD20 million in funding to develop and produce its next-generation hybrid turbocharger for marine engines. The new turbocharger is expected to be released in 2025.
Key Market Players
- ABB Ltd
- BorgWarner Inc
- Cummins Inc
- Garrett Motion Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery & Engine Co., Ltd.
- Napier Turbochargers Ltd.
- Rolls-Royce Plc
- Turbocharger and Engineering Company (TEC)
- Accelleron
|
By Engine Layout |
By Operation |
By Application |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Water Tube Industrial Boiler Market Size By Capacity, By Application (Food Processing, Pulp & Paper, Chemical, Refinery,...
- U.S. Industrial Boiler Market Size By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Capacity, By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condens...
- Fire Tube Industrial Boiler Market - By Capacity (<10 MMBtu/hr, 10-25 MMBtu/hr, 25-50 MMBtu/hr, 50-75 MMBtu/hr, >75 MMBt...
- Gas Fired Boiler Market Size - By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 - 100 MMBtu/hr, > 100 - 250 MMBtu/...
- Europe Residential Boiler Market Size - By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural ...
- U.S. Boiler Market Size By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), Capacity, By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), By Produ...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Snapshot
-
1.2 Key Developments and Trends
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Scope and Objectives of the Report
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Functional Overview of Hybrid Turbochargers
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What Are Hybrid Turbochargers?
-
3.2 Comparison with Conventional Turbocharging Systems
-
3.3 Role in Improving Fuel Efficiency and Emissions Compliance
-
3.4 Value Chain Analysis in the Marine Propulsion Industry
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Drivers
-
4.1.1 Stringent IMO Regulations on Maritime Emissions
-
4.1.2 Rising Demand for Fuel-Efficient Propulsion in Commercial Vessels
-
4.1.3 Growing Fleet Electrification and Hybridization Initiatives
-
-
4.2 Restraints
-
4.2.1 High System Integration and Retrofit Costs
-
4.2.2 Limited Awareness in Smaller Vessel Segments
-
-
4.3 Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Integration with Electric Assist and Waste Heat Recovery Systems
-
4.3.2 Potential Adoption in Naval and Offshore Support Vessels
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 System Architecture and Energy Recovery Mechanisms
-
5.2 Power Assist Turbocharging (PAT) and E-Booster Technologies
-
5.3 Control Strategies and Power Electronics Integration
-
5.4 Compatibility with Dual-Fuel and LNG Marine Engines
-
5.5 Maintenance, Durability, and Lifecycle Considerations
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Vessel Type
-
6.1.1 Cargo Ships
-
6.1.2 Tankers
-
6.1.3 Container Ships
-
6.1.4 Naval Vessels
-
6.1.5 Offshore Support Vessels
-
-
6.2 By Engine Type
-
6.2.1 2-Stroke Engines
-
6.2.2 4-Stroke Engines
-
6.2.3 Dual-Fuel Engines
-
-
6.3 By Deployment
-
6.3.1 Newbuild Installations
-
6.3.2 Retrofit Projects
-
-
-
Regional Analysis
-
7.1 Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea)
-
7.2 Europe (Germany, Norway, Netherlands)
-
7.3 North America (U.S., Canada)
-
7.4 Middle East & Africa
-
7.5 Latin America
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue and Unit Shipment Forecast
-
8.2 Segment-Wise and Regional Growth Analysis
-
8.3 Market Penetration in Green Marine Initiatives
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share and Strategic Positioning
-
9.2 Key Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 ABB Turbocharging (Accelleron)
-
9.2.2 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery & Equipment
-
9.2.3 MAN Energy Solutions
-
9.2.4 Kawasaki Heavy Industries
-
9.2.5 Napier Turbochargers
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Partnerships, Pilot Projects, and Product Innovations
-
-
Regulatory and Environmental Framework
-
10.1 IMO MARPOL Annex VI and Tier III Standards
-
10.2 EU and U.S. Green Shipping Policies
-
10.3 Ship Classification Requirements and Approval Processes
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 Electrified Boosting Systems in Hybrid Marine Propulsion
-
11.2 Digital Twins and Predictive Diagnostics for Turbochargers
-
11.3 Long-Term Role in Decarbonization of Deep-Sea Shipping
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 References and Sources
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
