China Fuel Cell Market
China Fuel Cell Market By Type (Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC), Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC), Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC), Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC), Others), By Application (Portable, Stationary, Vehicle), By Size (Small and Large), By End User (Residential, Transportation, Data Center, Military & Defense, Others), By Region, Competition, Forecast and Opportunities 2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
| Market Size (2022) | USD 1.32 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 17.10% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) |
| Largest Market | East |
Market Overview
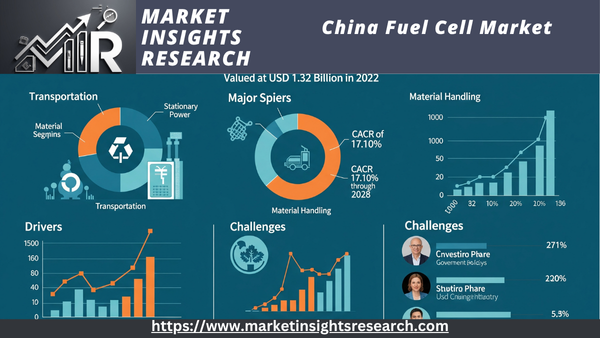
The China Fuel Cell Market, valued at USD 1.32 Billion in 2022, is poised for robust growth in the forecast period, exhibiting a substantial CAGR of 17.10% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Introduction to Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that use a carefully regulated reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent to transform chemical energy from a fuel—usually hydrogen—into electrical energy. Fuel cells are a very clean and effective energy source because of their special procedure, which avoids combustion and produces very little pollution. Hydrogen molecules are converted into protons and electrons inside a fuel cell. An electric current is created when protons go through an electrolyte and electrons move through an external circuit. Oxygen works with protons and electrons at the cathode to create water while releasing more energy. Among the many benefits of fuel cells are their high efficiency, low environmental impact, and quiet operation. They find use in a variety of fields, including transportation (including fuel cell cars), portable electronics, and stationary power generation for homes and businesses. Fuel cells are essential for lowering greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on fossil fuels, which advances sustainable energy solutions in a variety of industries.
Key Market Drivers
Strategic Energy Diversification and Clean Energy Commitments
China's strategic mandate to diversify its energy landscape and meet aggressive clean energy targets is driving the country's fuel cell sector. China, a rising economic powerhouse with rising energy needs, understands how urgent it is to reduce its dependency on traditional fossil fuels and shift to sustainable and eco-friendly energy sources. A key component of this motivation is the Chinese government's unwavering resolve to increase the share of renewable energy in its energy mix. This pledge is reinforced by China's wealth of renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, which can all be used to produce hydrogen and then use it in fuel cells.
By adopting fuel cell technology, China may expand its energy horizons in a dynamic approach that promotes environmental stewardship and adaptability to changing energy dynamics. Fuel cells are a versatile and durable solution that may provide dependable and environmentally friendly power in a variety of industries, including transportation, electricity generation, and remote energy access. Fuel cells' alignment with China's clean energy goals solidifies their position as a key driver of the country's transition to sustainability.
Furthermore, by reducing its reliance on imported fossil fuels, the use of fuel cell technology significantly improves China's energy security. As domestic hydrogen production capacities develop and fuel cell technology progresses, China is poised to achieve greater energy self-sufficiency. As a result, China is better equipped to handle energy-related uncertainty and is less vulnerable to the whims of international energy markets. In this regard, fuel cells become more than just scientific advancements; rather, they become strategic cornerstones that increase energy diversification, strengthen security, and highlight China's steadfast dedication to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Urbanization and the Paradigm Shift toward Sustainable Mobility
A major factor driving China's fuel cell market is the urgent need for creative and sustainable mobility solutions, which is highlighted by the country's fast urbanization and growing urban population. Fuel cells appear as a revolutionary force in line with China's urban development objectives as metropolitan areas struggle with increasing traffic congestion, declining air quality, and the need for effective mobility. The revolutionary potential of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), which have the ability to completely change urban transportation, is a key motivator. FCVs are a strong substitute for conventional internal combustion engine vehicles in the context of China's sincere attempts to improve air quality and reduce emissions. Fuel cells, which emit only water vapor, are the pinnacle of zero-emission mobility and help to improve urban ecosystems and the quality of the air. Strong government support for EVs and the development of charging infrastructure at the same time demonstrate China's dedication to sustainable mobility. With their longer driving ranges and quicker refilling periods than battery electric vehicles, FCVs provide a workable way to deal with range anxiety and charging issues that are common in electric mobility. The adaptability of fuel cell technology goes beyond private automobiles to include business delivery fleets, buses, and taxis, among other urban transportation alternatives. This wide range of possible applications highlights how crucial fuel cells will be in determining how China's urban transportation system develops in the future. China's use of fuel cell technology to address the needs of sustainable transportation has two benefitsit reduces pollution and urban congestion while accelerating the shift to cleaner and more effective energy use. The growing popularity of fuel cell-powered automobiles aligns well with China's goals for urban development, resulting in a more sustainable, livable, and prosperous urban environment.
Economic Development Catalyst and Pinnacle of Technological Advancement
Fuel cells serve as engines for China's economic growth and scientific advancement, blending in well with the country's ambitions to become a global leader in both industry and technology. Fuel cell technology is emerging as a revolutionary force for promoting innovation, creating jobs, and drawing investments in high-tech industries as China works to improve its industrial capacities. The main motivator is China's potential to become a regional hub for fuel cell manufacture, research, and development. China is at the forefront of fuel cell innovation thanks to wise investments in research facilities and strong industry-academia partnerships. By attracting both domestic and foreign capital, this stimulus not only accelerates technological improvement but also stimulates economic growth. From research and development to manufacture, installation, and maintenance, the fuel cell industry is a hub for job possibilities along the whole value chain. This increase in employment opportunities greatly improves the socioeconomic fabric of China by equipping its workers with specialized knowledge and skills in cutting-edge renewable energy technology. Furthermore, fuel cells promote innovation in a variety of industries, extending beyond their immediate field. Fuel cell technology spurs advances in materials science, engineering, and energy management that spread to other industries, establishing China as a worldwide innovation hub and fostering a culture of constant invention. In addition to enhancing its technological capabilities, China presents itself as a dynamic contributor to the global innovation scene by adopting fuel cell technology as a cornerstone for economic development and innovation. This force pulls China toward long-term economic expansion, technological superiority, and a prosperous future built on innovative clean energy technologies.
Supportive policies and Regulations are Likely to Propel the Market
National Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Development Plan
The National Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Development Plan is a prime example of China's aggressive strategy to expand its fuel cell business. The foundation for the fuel cell industry's rapid expansion and innovation is laid by this all-encompassing policy framework. The plan acts as a blueprint for maximizing the potential of fuel cells across a range of industries and strategically aligns with China's commitment to a sustainable energy transition. The Chinese government provides fuel cell producers, researchers, and developers with significant tax breaks, research grants, and financial incentives under this strategy. The objectives of this financial assistance are to encourage private sector involvement, strengthen domestic manufacturing capabilities, and boost research and development efforts. Additionally, the plan places a high priority on building a strong infrastructure for hydrogen, which includes facilities for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution as well as a network of fuel cell vehicle (FCV) recharging stations. The strategy promotes cooperative alliances between public and private organizations to hasten adoption even more. This strategy encourages the development of a competent workforce, technological innovation, and knowledge sharing. China is advancing its fuel cell market toward self-sufficiency, worldwide competitiveness, and a sustainable energy future with this policy.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Renewable Energy Integration and Power Generation Incentives
China's dedication to power generation incentives and the integration of renewable energy sources is crucial to the growth of its fuel cell business. Fuel cells and other clean energy technologies must be given priority status in terms of grid access, pricing, and subsidies under the government's Renewable Energy Law and related regulations. The Chinese government encourages the integration of fuel cells into the electrical grid by offering attractive feed-in tariffs and other financial incentives. This strategy gives fuel cell power generation plants a steady flow of income, which boosts investor confidence and propels market expansion. Furthermore, the widespread use of fuel cells is boosted by China's strong support for renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Electrolysis can be used to create hydrogen from excess renewable energy, which can subsequently be used in fuel cells to generate electricity or for other purposes. Grid stability, overall efficiency, and energy reliability are all improved by this integration. China's regulations encourage the growth of fuel cell power generation by enabling the smooth integration of fuel cells into the renewable energy landscape, which helps create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix.
Research and Development Collaboration and International Cooperation
Key Market Challenges
Scaling Up Hydrogen Production and Infrastructure
The market for fuel cells in China has a lot of promise, but building a strong hydrogen infrastructure and increasing hydrogen output are major obstacles. The availability of a reliable and easily available source of hydrogen is essential to the success of fuel cell technology, and this requires solving numerous challenges in the infrastructure for manufacturing, delivery, and refilling. The need to produce enough hydrogen in a way that is both economical and environmentally sustainable is a difficulty for scaling up hydrogen production. The very environmental objectives that fuel cells seek to accomplish are compromised by the fact that current hydrogen synthesis techniques, including steam methane reforming, frequently rely on fossil fuels. A potential remedy is to switch to green hydrogen, which is created by electrolysis driven by renewable energy. However, significant financial outlays and careful planning are needed to implement electrolyzers and renewable energy sources at a scale that will facilitate the broad use of fuel cells. Furthermore, the establishment of a vast network of hydrogen production facilities, storage options, and refueling stations is a necessary component of the development of a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure. This infrastructure's establishment will need large capital expenditures and collaboration between a number of parties, including the government, energy suppliers, and commercial businesses. Finding a balance between the rate of fuel cell deployment and the growth of the hydrogen infrastructure is the difficult part. Another issue is public acceptability and awareness of fuel cell technology, especially when it comes to transportation. Addressing issues with range anxiety, accessibility to refilling, and the general convenience of utilizing fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) in comparison to traditional vehicles is necessary to persuade people to use FCVs. It will need significant marketing and education initiatives to dispel these myths and emphasize the benefits of FCVs, such as their zero-emission profile, quick recharging times, and ability to improve air quality. A thorough and well-coordinated effort is necessary to overcome these obstacles. To hasten the establishment of a strong hydrogen ecosystem, government regulations and incentives that favor green hydrogen generation are essential, as are smart alliances between public and private organizations. Working together can expedite the manufacturing, delivery, and refueling of hydrogen, which will accelerate the expansion of the fuel cell market in China. China can advance its clean energy transition and establish itself as a global leader in fuel cell technology by tackling the problem of scaling up infrastructure and hydrogen production.
Segmental Insights
Transportation
In 2022, the transportation segment took the lead in the fuel cell market, and it is anticipated to stay that way for the duration of the forecast. Air pollution and traffic congestion are major problems in China's heavily populated cities. Fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), which offer zero-emission transportation, have the potential to completely transform urban mobility. By exclusively emitting water vapor, FCVs help to lower greenhouse gas emissions and enhance air quality. FCVs can be crucial in reducing urban traffic and improving citizens' quality of life as cities place a higher priority on environmentally friendly transportation options. Compared to battery electric cars, FCVs have a clear advantage in terms of driving range and refueling durations. Concerns about range anxiety and charging infrastructure are addressed by FCVs' longer ranges and faster recharging, which makes them a viable solution for China's diverse and expansive terrain, including long-distance travel and rural transportation. The use of fuel cell technology is a natural fit with China's dedication to electric buses and the modernization of its public transportation infrastructure. FCVs offer effective and sustainable solutions for urban transportation and mass transit when used as buses, taxis, and other commercial vehicles. The use of FCV fleets has the potential to greatly lower emissions and advance environmentally friendly urban transportation.
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
In 2022, the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) segment took the lead in the fuel cell market, and it is anticipated to continue to do so.
Regional Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, Eastern China is the dominant region in the Chinese fuel cell market. With more than 1.4 billion people, Eastern China is the most populated region in China. This is caused by a number of reasons, including population density. This indicates that fuel cell applications, such power generation and transportation, have a sizable potential market. Furthermore, the Chinese government has put in place a variety of measures to encourage the use of fuel cell technology and supports its advancement. The Hydrogen Energy Development Plan is one of these, with the goal of China being a major producer and consumer of hydrogen by 2030. Renewable energy sources like sun and wind power are plentiful in eastern China and can be utilized to create hydrogen for fuel cells.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In March 2022, the Chinese government announced that it would invest USD 10 billion in a new hydrogen production and distribution network. The network is expected to be completed by 2025 and will help to support the development of the fuel cell market.
- In February 2022, the SAIC Motor Corporation announced that it would invest USD 1 billion in a new fuel cell production plant. The plant is expected to be completed by 2023 and will produce fuel cells for SAIC's hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
- In January 2022, the Hyundai Motor Company announced that it would invest USD 500 million in a new fuel cell research and development center in China. The center is expected to create 1,000 new jobs and will focus on developing new fuel cell technologies for vehicles and stationary applications.
- In December 2021, the Toyota Motor Corporation announced that it would invest USD 300 million in a new fuel cell production plant in China. The plant is expected to be completed by 2023 and will produce fuel cells for Toyota's hydrogen vehicles that use fuel cells.
- In November 2021, the China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) announced that it would invest USD 200 million in a new hydrogen production plant. The plant is expected to be completed by 2022 and will produce hydrogen for CNPC's fuel cell applications.
- These are just some of the recent investments in the fuel cell market in China in 2022. The Chinese government and private companies are increasingly investing in fuel cell technology, as they see it as a key part of the future of clean energy.
Key Market Players
- Beijing SinoHytec Co Ltd
- Tianneng Holding Group
- Ceres Power Holdings
- Weichai Power Co., Ltd.
- Shanghai Shenli Technology Co., Ltd
- Guangdong Guohong Hydrogen Energy Technology
- Beijing Sinohytec Co Ltd.
|
By Type |
By Application |
By Size |
By End User |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- U.S. Commercial Boiler Market – By Product (Hot Water, Steam), Application (Offices, Healthcare Facilities, Educationa...
- North America Commercial Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity, By Technology (Co...
- Water Tube Industrial Boiler Market Size By Capacity, By Application (Food Processing, Pulp & Paper, Chemical, Refinery,...
- U.S. Industrial Boiler Market Size By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Capacity, By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condens...
- Fire Tube Industrial Boiler Market - By Capacity (<10 MMBtu/hr, 10-25 MMBtu/hr, 25-50 MMBtu/hr, 50-75 MMBtu/hr, >75 MMBt...
- Gas Fired Boiler Market Size - By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 - 100 MMBtu/hr, > 100 - 250 MMBtu/...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Snapshot
-
1.2 Key Developments and Forecast Trends
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Scope and Purpose of the Report
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Classification
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What Are Fuel Cells?
-
3.2 Fuel Cell Technology Types and Working Principles
-
3.3 China's Strategic Role in the Global Fuel Cell Market
-
3.4 Market Evolution in Context of Hydrogen Economy
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Market Drivers
-
4.1.1 Government Policies and Hydrogen Infrastructure Initiatives
-
4.1.2 Commercialization of Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
-
4.1.3 Industrial Demand for Clean Backup and Remote Power
-
-
4.2 Market Restraints
-
4.2.1 High Cost of Fuel Cell Systems and Hydrogen Distribution
-
4.2.2 Limited Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure
-
-
4.3 Market Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Integration into Industrial Clusters and Smart Ports
-
4.3.2 Strategic Collaborations with Japan and Korea in PEMFC R&D
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
-
5.2 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC)
-
5.3 Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC)
-
5.4 Direct Methanol Fuel Cell (DMFC)
-
5.5 Hydrogen Fuel Generation, Compression, and Storage Solutions
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Fuel Cell Type
-
6.1.1 PEMFC
-
6.1.2 SOFC
-
6.1.3 Others
-
-
6.2 By Application
-
6.2.1 Transportation (Buses, Trucks, Trains, Forklifts)
-
6.2.2 Stationary Power (Primary and Backup)
-
6.2.3 Portable Power (Consumer Electronics, Drones)
-
-
6.3 By End-User
-
6.3.1 Automotive and Mobility
-
6.3.2 Energy and Utilities
-
6.3.3 Industrial & Commercial Buildings
-
6.3.4 Others
-
-
-
Regional Market Trends in China
-
7.1 East China (Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang)
-
7.2 South China (Guangdong, Shenzhen)
-
7.3 North China (Beijing, Hebei)
-
7.4 Central and Western Regions
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue and Unit Forecast by Region and Segment
-
8.2 FCEV Deployment Trends and Industrial Adoption
-
8.3 Hydrogen Supply Chain Expansion Forecast
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share of Leading Players
-
9.2 Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 SinoHytec
-
9.2.2 Shanghai Refire Technology
-
9.2.3 Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies
-
9.2.4 Weichai Power
-
9.2.5 Ballard Power Systems (Joint Ventures in China)
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 R&D Ecosystem and Local Supply Chain Mapping
-
-
Policy and Regulatory Framework
-
10.1 National Hydrogen Strategy (2021–2035)
-
10.2 Local Pilot Zone Initiatives and Subsidies
-
10.3 Standards for Fuel Cell Testing, Certification, and Deployment
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 China’s Role in Global Fuel Cell Supply Chains
-
11.2 Low-Cost Catalyst Development and Durability Enhancements
-
11.3 Fuel Cells in Maritime, Aerospace, and Emerging Mobility
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 References and Sources
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
