Renewable Battery Storage Market
Renewable Battery Storage Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Type (Wind Power, Hydroelectric Power, Solar Power, Bio Energy, Others), By End User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial), By Region, By Competition 2018-2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
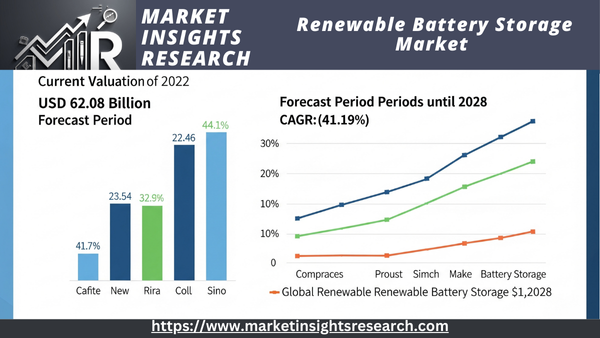
| Market Size (2022) | USD 62.08 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 41.19% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Industrial |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
Market Overview
The Global Renewable Battery Storage Market was valued at USD 62.08 billion in 2022 and is projected to experience robust growth in the forecast period with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)1 of 41.19% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
The global Renewable Battery Storage market is the rapidly growing sector within the renewable energy industry that focuses on the development, production, deployment, and utilization of energy storage systems in conjunction with renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These energy storage systems, often utilizing advanced battery technologies, are a crucial enabler for the efficient capture, storage, and subsequent distribution of renewable energy.
Essentially, this market centers around the integration of energy storage solutions, particularly batteries, into renewable energy projects and electricity grids. The primary goal is to address the inherent intermittency and variability of renewable sources, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply. This market covers various applications, from residential and commercial-scale installations to large utility-scale projects, all aimed at optimizing energy generation, consumption, and grid management.
Driven by the global shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, combined with the need for grid stability and flexibility, the Renewable Battery Storage market plays a pivotal role in facilitating the transition away from fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and fostering a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure worldwide.
Key Market Drivers
Growing Renewable Energy Capacity and Intermittency Management
The robust growth of the global Renewable Battery Storage market is significantly fueled by the rapid expansion of renewable energy capacity worldwide. As countries aim to lower their carbon footprint and shift to cleaner energy sources, investments in solar and wind power are increasing. However, the intermittent nature of these renewables makes battery storage systems essential for managing and storing excess energy for later use, thereby stabilizing energy grids.
Renewable battery storage solutions, like lithium-ion batteries, offer a reliable way to store surplus energy from high renewable generation periods. This stored energy can then be used when renewable generation is low, ensuring a consistent power supply. As governments and utilities prioritize integrating renewables, the demand for battery storage is indeed set to rise substantially.
Falling Battery Costs and Technological Advancements
The decreasing expenses associated with battery technologies, coupled with continuous progress in energy storage systems, are key factors fueling the expansion of the global Renewable Battery Storage market. Over the past decade, the price of lithium-ion batteries, the predominant technology in this sector, has notably decreased, primarily due to economies of scale, enhanced manufacturing techniques, and intensified research and development efforts.
Moreover, ongoing technological innovations are improving the efficiency and performance of renewable battery storage solutions. These advancements include enhancements in battery chemistry, energy density, lifespan, and safety features. As batteries become more cost-effective and technologically sophisticated, they present a more compelling and practical solution for integrating with renewable energy sources, thereby further driving market growth.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Energy Transition and Climate Change Mitigation
The pressing imperative to curb climate change and diminish greenhouse gas emissions stands as a significant catalyst for the global Renewable Battery Storage market. Across the globe, governments and organizations are dedicated to achieving ambitious goals for renewable energy adoption and carbon footprint reduction. In this crucial undertaking, battery storage plays a vital role by facilitating the effective utilization of renewable energy, lessening our dependence on fossil fuels, and ensuring the stability of energy grids.
Energy storage enables a more efficient alignment of energy supply and demand, thereby reducing the necessity for backup power plants fueled by fossil fuels, which are often employed to compensate for the intermittent nature of renewable energy. This transition towards cleaner energy sources, coupled with the widespread integration of renewable battery storage technologies, aligns with global initiatives aimed at limiting global warming and transitioning towards a sustainable energy future.
Increasing Electrification and Decentralization
The growing electrification of diverse sectors, including transportation and heating, constitutes another significant driver for the global Renewable Battery Storage market. With the rising popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing adoption of electric heat pumps over traditional heating systems, the demand for electricity is escalating. Renewable battery storage systems are instrumental in managing and balancing this heightened electricity demand, thereby ensuring a dependable power supply.
Furthermore, there's a growing trend towards decentralization in energy production, with more homes and businesses installing solar panels and small-scale wind turbines. These distributed energy resources can be paired with battery storage to optimize self-consumption and lessen reliance on the central grid. As electrification and decentralization continue their upward trajectory, renewable battery storage solutions are becoming indispensable for maximizing energy utilization and alleviating grid congestion.
Grid Resilience and Reliability
Enhancing grid resilience and reliability has become a paramount concern for utilities and governments globally. The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, coupled with the threat of cyberattacks and other disruptions, poses significant risks to power infrastructure, potentially leading to widespread outages that impact businesses and communities alike. Renewable battery storage systems play a crucial role in bolstering grid resilience by providing essential backup power during emergencies and significantly enhancing overall grid stability.
By integrating energy storage solutions, utilities gain the capability to store surplus energy generated during periods of low demand and strategically release it when needed most. This critical function helps to prevent both complete blackouts and partial brownouts, ensuring a more consistent power supply. This enhanced reliability not only provides direct benefits to consumers but also offers significant advantages to grid operators, creating a strong incentive for further investment in robust renewable battery storage infrastructure.
Favorable Regulatory and Policy Environment
A supportive regulatory and policy environment acts as a significant catalyst for the global Renewable Battery Storage market. Across the globe, governments are enacting favorable policies and incentives designed to encourage the adoption of both renewable energy and energy storage technologies. These often include direct financial incentives, tax credits, and the establishment of ambitious renewable energy targets.
Moreover, as nations strive to modernize their existing energy grids and significantly reduce emissions, they are actively promoting the integration of battery storage systems through the implementation of updated grid codes and regulations. This proactive regulatory support serves to lower the barriers to entry for new battery storage projects and effectively encourages increased private investment within the sector.
In conclusion, the rapid expansion of the global Renewable Battery Storage market is fueled by a powerful convergence of key factors. These include the continuous growth of renewable energy generation capacity, the steadily decreasing costs of battery technologies, the urgent global efforts to mitigate climate change, increasing electrification across various sectors, the critical need for enhanced grid resilience, and the establishment of supportive regulatory frameworks. Together, these drivers are paving the way for the widespread adoption of renewable battery storage solutions, ushering in a more sustainable and resilient energy future.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government Policies are Likely to Propel the Market
Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards
Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards (REPS), also referred to as Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), represent a crucial government policy propelling the global Renewable Battery Storage market. REPS are regulations that require utilities to generate a defined portion of their electricity from renewable energy sources by a designated future date. These standards are specifically designed to promote the utilization of renewable energy and, consequently, the adoption of energy storage technologies.
Under the framework of REPS, utilities are provided with incentives to invest in renewable energy projects, such as solar and wind farms, and to incorporate renewable battery storage systems to guarantee a stable and consistent energy supply. This policy not only contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions but also stimulates innovation within battery technology as utilities actively seek efficient methods to store and utilize the energy generated from renewable sources.
Investment Tax Credits and Incentives
Indeed, numerous governments are leveraging investment tax credits (ITCs) and various financial incentives to spur investment in renewable battery storage systems. These strategic policies effectively lower the initial capital outlay for both businesses and homeowners seeking to integrate energy storage solutions. Typically, ITCs offer a reduction in income tax liability calculated as a percentage of the energy storage system's cost.
A prime example is the federal Investment Tax Credit in the United States for solar energy systems, which can also be applied to installations that combine solar power with energy storage. Such impactful incentives actively encourage individuals, businesses, and utilities to deploy battery storage systems, thereby significantly boosting the overall market demand for these crucial technologies.
Feed-in Tariffs and Power Purchase Agreements
feed-in tariffs (FiTs) and power purchase agreements (PPAs) are important government policies that establish attractive pricing structures for those generating renewable energy. FiTs ensure a set payment for each unit of renewable energy produced, while PPAs provide long-term contracts at pre-determined rates. These policies create a predictable and stable revenue stream for renewable energy projects, making them more financially appealing to investors.
Renewable battery storage plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of both FiTs and PPAs. By allowing renewable energy producers to store surplus energy generated during peak production times and then sell it when demand and prices are higher, battery storage enhances the overall profitability of these projects. Furthermore, by increasing the reliability and consistency of renewable energy supply, battery storage systems make these policies even more attractive to both project developers and financial institutions.
Grid Modernization and Integration Mandates
In order to handle an increasing proportion of renewable energy sources, governments around the world are realizing the necessity of updating their outdated electrical systems. In order to better integrate renewable energy and storage technologies, utilities must upgrade their infrastructure in accordance with grid modernization and integration standards.
These regulations frequently mandate that utilities deploy battery storage devices to show grid resilience and dependability. Since energy storage systems are essential for preserving grid stability while incorporating fluctuating renewable energy sources, government funding for grid modernization fosters a climate that is conducive to their deployment.
Research and Development Funding
Innovation in renewable battery storage systems is greatly aided by government-sponsored research and development (R&D) financing programs. Governments promote the development of battery chemistry, energy density, safety, and cost-effectiveness by funding research and development. These developments result in energy storage technologies that are more economical and effective.
To speed up the development of battery technology, governments may form alliances with academic institutions and private businesses in addition to providing direct R&D funding. Governments support the general expansion and competitiveness of the renewable battery storage market by encouraging innovation in the energy storage industry.
Environmental Regulations and Emissions Reduction Targets
By promoting cleaner and more sustainable energy systems, environmental rules and emissions reduction targets are propelling the global market for renewable battery storage. Utilities are moving away from fossil fuels and toward renewable energy sources combined with energy storage as a result of governments establishing strict emissions reduction targets to fight climate change.
Through the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources and the creation of a more adaptable and responsive energy infrastructure, battery storage systems contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The need for renewable battery storage solutions will only increase as governments tighten emissions laws and set specific goals, supporting the global transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy systems.
In conclusion, the global market for renewable battery storage is significantly shaped by government policies like as feed-in tariffs, investment tax credits, grid modernization requirements, research and development funding, Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards, and environmental restrictions. By offering incentives, opening up markets, and hastening the adoption of energy storage technologies, these policies help ensure a more robust and sustainable energy future.
Key Market Challenges
Energy Storage Costs and Scalability
The price of energy storage systems and the scalability of these technologies are two of the main issues confronting the global industry for renewable battery storage. Even while battery prices have significantly decreased, they still account for a sizeable amount of the total cost of renewable energy installations. The broad use of renewable battery storage may be hampered by this expense, particularly in areas with little financial resources.
The materials utilized in battery production, manufacturing procedures, and economies of scale are some of the elements that contribute to the cost barrier. Even though economies of scale have helped to lower costs, more advancements are required to make energy storage technologies more widely available and reasonably priced for a wider range of uses.
Scalability is also an important factor to take into account when implementing renewable battery storage. The energy output and consumption needs of a particular area or application must be met by the capacity of energy storage systems. It can be difficult to achieve scalability, especially for large-scale utility projects that call for enormous battery arrays.
Continuous research and development is necessary to find more affordable materials and production techniques in order to overcome these issues. Higher energy densities and reduced prices can result from advancements in battery chemistry and design. To promote investment in energy storage research, development, and deployment, governments and industry stakeholders must collaborate to create policies and incentives. Additionally, standardizing battery components and systems helps lower costs and streamline production.
Grid Integration and Regulatory Hurdles
Overcoming regulatory obstacles and integrating energy storage devices into current electrical grids present another major issue for the worldwide industry for renewable battery storage. Optimizing the advantages of renewable battery storage, such as increasing grid resilience and facilitating a wider penetration of renewable energy, requires effective integration.
Technical problems pertaining to grid compatibility, voltage regulation, and system stability are among the hurdles associated with grid integration. For energy to be efficiently stored, dispatched, and distributed, battery storage devices and the grid must work together fluidly. Grid instability and reduced dependability may result from ineffective energy storage integration.
The adoption of renewable battery storage is made more difficult by regulatory obstacles. These obstacles may include a variety of things, such as market rules, connectivity standards, and permitting procedures. Project developers may experience delays and uncertainty as a result of current regulations' inability to appropriately address the special features of energy storage systems.
Governments and regulatory agencies must revise and modify their regulations to take into account the expanding importance of energy storage in the energy landscape in order to overcome these obstacles. Energy storage development can be facilitated and investor uncertainty can be decreased via streamlined permitting procedures, uniform connectivity standards, and transparent market regulations.
To guarantee the smooth integration of energy storage devices, grid operators and utilities must also make investments in modifications to the grid's infrastructure. This could entail modifying current transmission lines and substations to accommodate grid stability, voltage control, and bidirectional power flow.
In order to overcome both technical and regulatory difficulties, cooperation between stakeholders—including government agencies, utilities, industry actors, and research institutions—is essential. These obstacles can be addressed by collaborating to develop solutions and establish a favorable climate for renewable battery storage, which will allow the market to flourish and help ensure a more sustainable energy future.
Segmental Insights
Type Insights
In 2022, the Solar Power segment had the biggest market share. One of the most prevalent and plentiful renewable energy sources in the world is solar energy. Since the sun shines almost everywhere on Earth, a large number of places and nations can use solar electricity. The extensive use of solar panels and photovoltaic (PV) systems is made possible by the abundance of solar resources. Because of economies of scale, improved production efficiency, and technological breakthroughs, the price of solar PV panels has been gradually declining over time. The adoption of solar electricity has increased as a result of this cost reduction. Solar photovoltaic systems are very scalable and modular. They are appropriate for a range of uses, from utility-scale projects to residential ones, and can be incorporated into existing infrastructure or placed on rooftops or open spaces. This adaptability makes it possible for people, companies, and utilities to install solar power systems in different locations and according to their unique requirements. Numerous nations have put in place advantageous policies that promote the use of solar energy, such as feed-in tariffs and net metering. By "storing" extra electricity produced by their solar panels for future usage as credit, net metering enables businesses and homeowners to sell it back to the grid. Feed-in tariffs give solar system owners financial incentives by guaranteeing set payments for solar power generation. Because it depends on the availability of sunshine, solar power generation is by its very nature sporadic. Batteries and other energy storage devices are frequently used into solar PV systems to increase the dispatchability and dependability of solar energy. To provide a steady supply of power, these batteries store extra energy produced during sunny spells and release it at night or on overcast days. One clean, renewable energy source that emits no greenhouse gases when in use is solar power. People and organizations looking to lessen their carbon footprint and support cleaner energy choices will find this environmental sustainability appealing. The overall performance and dependability of solar power systems have been enhanced by continuous developments in energy storage and solar panel efficiency. Due to these developments, solar energy is now more competitive with other renewable energy sources and conventional fossil fuels. Many governments worldwide offer incentives, tax credits, and subsidies to promote solar power adoption. These policies reduce the initial costs of solar installations and enhance the return on investment for solar system owners.
End User Insights
In 2022, the biggest market share was held by the residential segment. A growing number of homeowners are eager to become somewhat energy independent and less dependent on conventional utility providers. They can lessen their reliance on electricity from the grid by using renewable battery storage devices to store extra energy produced by rooftop solar panels and use it when needed. Residential customers frequently have to deal with peak demand fees and variable electricity rates. Homeowners can improve their energy use patterns by combining energy storage, like home battery systems, with renewable energy sources. Over time, they can save a substantial amount of money by storing extra energy during periods of low power rates and using it during times of peak electricity costs. Many homeowners are looking for cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions as a result of growing environmental consciousness and worries about climate change. In line with eco-conscious ideals, solar panels and energy storage not only minimize electricity costs but also carbon emissions. Governments in many nations provide tax breaks, rebates, incentives, and advantageous net metering laws to promote the use of energy storage and renewable energy in homes. Homeowners can now afford to invest in these technologies thanks to these financial advantages, which helps explain their market dominance. A certain amount of resilience against power disruptions is offered by energy storage. In the event of a grid outage, residential battery systems can serve as backup power sources, guaranteeing that vital appliances and systems keep running. Interest in domestic energy resilience has increased due to the growing frequency of extreme weather events and grid vulnerability. Home energy storage devices are becoming more dependable and affordable thanks to advancements in battery technology. For example, lithium-ion batteries have gained popularity because of their high energy density, extended cycle life, and falling costs. Generally speaking, residential renewable battery storage systems are made to be simple to install and integrate with pre-existing solar PV systems. Because of its simplicity of installation, a wider variety of homeowners can now use it without having to make significant changes to their homes. Neighbors and early adopters who embrace energy storage and renewable energy can encourage others to do the same. The installation of home battery systems and solar panels by more households may have a "neighborhood effect," promoting further residential adoption. Smart energy management systems give homeowners the capacity to track and regulate their energy production and usage. These systems, which give consumers real-time data and control over their energy use, frequently come with domestic energy storage solutions.
Regional Insights
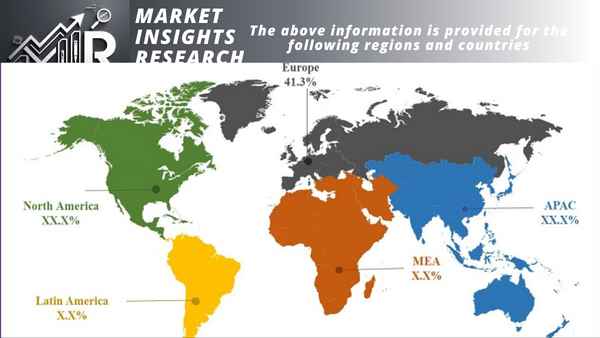
With more than 40% of the global market in 2022, Asia Pacific was the largest market for renewable battery storage. Some of the fastest-growing economies in the world are found in this region, and in order to sustain economic growth, there is an increasing need for battery storage and renewable energy. Asia Pacific's biggest market for renewable battery storage is China, which is followed by South Korea, Japan, and India.
With more than 30% of the global market in 2022, North America was the second-largest market for renewable battery storage. Some of the top markets for renewable energy in the world, including the US and Canada, are located in this region. Numerous factors, such as the growing use of renewable energy sources, the need to increase grid stability and reliability, and government policies that encourage the use of renewable energy and battery storage, are propelling the growth of the renewable battery storage market in North America.
With more than 20% of the global market in 2022, Europe ranked as the third-largest market for renewable battery storage. In order to facilitate the grid's integration of renewable energy, there is an increasing need for renewable battery storage, and the region has some of the most aggressive renewable energy goals in the world. Europe's biggest market for renewable battery storage is Germany, which is followed by France, Italy, and the United Kingdom.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In March 2023, LG Energy Solution announced an investment of USD 5.5 billion to build a battery manufacturing complex in Arizona, USA. The complex will produce lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries for energy storage systems (ESS) and cylindrical batteries for electric vehicles (EVs).
- In February 2023, Tesla announced that it would invest USD 3.6 billion to expand its Gigafactory Nevada to produce batteries for electric vehicles and stationary energy storage.
- In January 2023, Panasonic announced that it would invest USD 4 billion to build a new battery manufacturing plant in Kansas, USA. The plant will produce lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles and stationary energy storage.
- In December 2022, Hitachi ABB Power Grids announced that it would invest USD 500 million to build a new battery manufacturing plant in North Carolina, USA. The plant will produce lithium-ion batteries for stationary energy storage.
- In November 2022, Fluence Energy announced that it had raised USD 235 million in new funding to support its global expansion. The company is a leading provider of battery-based energy storage solutions.
Key Market Players
- ABB Group
- BYD Co. Ltd
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited
- Fluence Energy
- General Electric Company
- Hitachi ABB Power Grids
- LG Chem
- NEC Corporation
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
|
By Type |
By End User |
By Region |
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Residential Electric Boiler Market Size - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), Industry Analysis Report, Reg...
- Europe Steam Boiler Market - By Capacity, By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), ...
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Residential Boiler Market Size By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil,...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Overview
-
1.2 Key Developments and Insights
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Scope and Objectives
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Terminology
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What is Renewable Battery Storage?
-
3.2 Role in Solar, Wind, and Hybrid Energy Systems
-
3.3 Integration with Distributed and Utility-Scale Renewables
-
3.4 Value Chain and Ecosystem Mapping
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Market Drivers
-
4.1.1 Growing Investments in Renewable Energy Projects
-
4.1.2 Declining Battery Costs and Performance Improvements
-
4.1.3 Need for Grid Stability and Load Balancing
-
-
4.2 Market Restraints
-
4.2.1 Interconnection and Regulatory Hurdles
-
4.2.2 Environmental and Recycling Concerns
-
-
4.3 Market Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Energy Arbitrage and Demand Response Programs
-
4.3.2 Off-Grid and Rural Electrification Projects
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Lithium-Ion Battery Systems (LFP, NMC)
-
5.2 Flow Batteries and Long-Duration Storage
-
5.3 Solid-State and Sodium-Ion Technologies
-
5.4 Battery Management Systems and Inverters
-
5.5 Safety Mechanisms and Storage Integration Models
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Battery Type
-
6.1.1 Lithium-Based
-
6.1.2 Flow Batteries
-
6.1.3 Lead-Based
-
6.1.4 Others
-
-
6.2 By Application
-
6.2.1 Residential Solar + Storage
-
6.2.2 Commercial and Industrial (C&I)
-
6.2.3 Utility-Scale Storage
-
6.2.4 Off-Grid and Mini-Grids
-
-
6.3 By Deployment Mode
-
6.3.1 Front-of-the-Meter (FTM)
-
6.3.2 Behind-the-Meter (BTM)
-
-
-
Regional Market Analysis
-
7.1 North America
-
7.2 Europe
-
7.3 Asia-Pacific
-
7.4 Latin America
-
7.5 Middle East & Africa
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue Forecast by Segment and Region
-
8.2 Installed Capacity Growth Trends
-
8.3 Scenario Analysis and Demand Outlook
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share Analysis
-
9.2 Key Player Profiles
-
9.2.1 Tesla (Megapack, Powerwall)
-
9.2.2 Fluence
-
9.2.3 LG Energy Solution
-
9.2.4 BYD
-
9.2.5 CATL
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Collaborations
-
-
Policy and Regulatory Framework
-
10.1 Storage Incentives and Renewable Energy Mandates
-
10.2 Interconnection Guidelines and Grid Codes
-
10.3 Safety and Environmental Compliance Standards
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 AI-Powered Storage Optimization
-
11.2 Virtual Power Plants and Aggregation
-
11.3 Role in Net-Zero and Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Methodology and Assumptions
-
13.3 Sources and References
-
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
