Portable Fuel Cell Market
Portable Fuel Cell Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By DWT (PSV below 3000 DWT, PSV above 3000 DWT), By Applications (Oil and Gas Production, Offshore Construction, Military, Others), By Type (Cargo and Support), By fuel, (Diesel, LNG, Electric, Hybrid), By Region, By Competition 2018-2028
Published Date: June - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
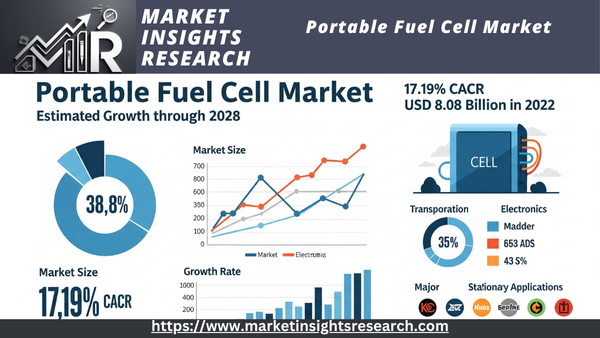
| Market Size (2022) | USD 8.08 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 17.19% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Automotive |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
Market Overview
The global portable fuel cell market was valued at USD 8.08 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period, with a CAGR of 17.19% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Key Market Drivers
Growing Demand for Clean Energy Solutions
Demand for portable fuel cells is rising globally, mostly due to the growing focus on sustainable and clean energy sources. The need to cut carbon emissions and move away from fossil fuels is becoming more pressing as environmental issues, climate change, and air pollution continue to garner media attention. Compared to conventional combustion engines and batteries, portable fuel cells provide a cleaner and more effective means of producing electricity, making them a promising solution.
Portable fuel cells are responding to the demand from both consumers and businesses for alternatives that emit fewer greenhouse gases. They offer a flexible and environmentally responsible power source that can be utilized in a range of applications, such as consumer electronics, backup power systems, and transportation. As governments and regulatory agencies tighten emissions standards and support green energy solutions, this demand is anticipated to continue and possibly rise.
Advancements in Fuel Cell Technology
The ongoing advancements in fuel cell technology are another important factor propelling the portable fuel cell market. Fuel cell efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness have all significantly increased as a result of ongoing research and development. Because of these technological developments, portable fuel cells are now a more appealing choice for both businesses and consumers.
Fuel cell performance has increased due to material innovations like proton exchange membranes and sophisticated catalysts. They can now compete with conventional power sources thanks to their longer runtimes, quicker refueling times, and enhanced durability. Further encouraging adoption is the fact that portable fuel cells are now more reasonably priced due to lower manufacturing costs.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government Incentives and Policies
Through the implementation of numerous incentives and policies, governments around the world are significantly contributing to the adoption of portable fuel cells. Businesses and individuals are being encouraged to invest in clean energy technologies, such as fuel cells, through the provision of subsidies, tax credits, and grants. These rewards aid in defraying startup expenses and promoting market expansion.
Additionally, industries are being compelled to investigate fuel cell applications as a way to comply with stringent environmental regulations and emissions reduction targets. In an effort to reduce costs and speed up technological advancements, governments are also funding research and development projects. The market for portable fuel cells is flourishing as a result of all these efforts.
Rising Demand for Mobile and Remote Power
The demand for portable fuel cells has been driven by the need for dependable power sources in isolated or off-grid areas. Fuel cells are perfect for situations where continuous power is essential because they have longer runtimes than conventional batteries and are simple to refuel. Applications for this trend include boats, remote industrial sites, and recreational vehicles.
Additionally, the growing demand for emergency response solutions and the popularity of outdoor recreational activities have fueled the adoption of portable fuel cells. Fuel cells are a preferred option in situations where conventional power sources might not be sufficient because of their adaptability and convenience.
Expansion of Hydrogen Infrastructure
The development of hydrogen infrastructure is a major factor propelling the portable fuel cell market, and hydrogen is essential to many fuel cell technologies. Hydrogen is becoming a more affordable and accessible fuel source for portable fuel cells as the infrastructure for its production, distribution, and storage grows.
Access to hydrogen fuel is becoming easier for businesses and consumers thanks to investments in hydrogen refueling stations, particularly in areas like Europe, Japan, and portions of North America. Furthermore, the creation of green hydrogen—which is generated using renewable energy sources like solar and wind—improves portable fuel cells' environmental credentials.
Emerging Markets and Industry Collaborations
The market for portable fuel cells is expanding significantly in emerging markets, especially in Asia-Pacific nations like South Korea and Japan. These countries are making significant investments in fuel cell technology for a range of uses, such as stationary power generation and transportation. Their dedication to clean energy and sustainability is propelling the market's notable growth.
Additionally, industry collaboration is promoting innovation and expanding market reach. Technology developers, energy firms, and fuel cell manufacturers are collaborating to create integrated solutions that serve a wider range of applications. These partnerships are crucial for increasing output, cutting expenses, and guaranteeing the market for portable fuel cells keeps expanding.
In conclusion, the need for clean energy solutions, government incentives, technological advancements, the need for mobile and remote power, the expansion of hydrogen infrastructure, and cooperative industry efforts are all contributing to the remarkable growth of the global portable fuel cell market. Together, these factors are propelling the market's growth and diversification, positioning portable fuel cells as a viable and sustainable energy source for the future.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government Policies are Likely to Propel the Market
Subsidies and Tax Incentives for Portable Fuel Cell Adoption
Globally, governments are realizing the value of sustainable and clean energy sources like portable fuel cells. Many governments have put in place tax breaks and subsidies for businesses and consumers to encourage their adoption. The initial high costs of acquiring and implementing portable fuel cells are intended to be partially offset by these policies.
In order to lower the upfront costs for people and businesses investing in fuel cell technology, subsidies can be in the form of direct financial assistance or rebates. On the other hand, tax incentives provide corporations or individuals who integrate portable fuel cells into their operations with exemptions or reductions in income taxes.
By increasing the economic appeal of portable fuel cells, these policies hope to increase market demand and accelerate the adoption of clean energy technologies.
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) and Clean Energy Targets
In order to increase the proportion of clean energy sources in their energy portfolios, numerous governments have set aggressive goals. They frequently use clean energy targets, also known as Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), which require a specific proportion of energy to come from renewable sources, such as portable fuel cells, in order to accomplish these goals.
These laws establish a framework for regulations that incentivize utilities and businesses to make investments in fuel cell technology and other cleaner energy sources. Since meeting these standards frequently necessitates ongoing innovation, they also motivate research and development efforts to increase the efficacy and efficiency of portable fuel cells.
Research and Development Grants
The significance of fuel cell technology in cutting greenhouse gas emissions and developing clean energy solutions is acknowledged by governments. Numerous governments provide grants and funding opportunities to universities, research institutions, and businesses involved in fuel cell research in order to encourage research and development in this area.
By addressing technical obstacles and lowering production costs, these grants aid in the development of new and enhanced portable fuel cell technologies. Governments hope to speed up the commercialization of fuel cell products by encouraging innovation, which will increase their accessibility for a greater range of sectors and uses.
Environmental Regulations and Emissions Standards
The adoption of portable fuel cells is directly impacted by strict emissions standards and environmental regulations. In an effort to lessen air pollution and fight climate change, governments frequently place restrictions on emissions from a range of industries and the transportation sector.
Companies and automakers may use portable fuel cells as a greener substitute for internal combustion engines in order to meet these regulations. Fuel cell technology adoption can be greatly accelerated by this policy-driven demand for cleaner energy sources, especially in industries where reducing emissions is a top priority.
Investment in Hydrogen Infrastructure
One important government initiative that promotes the expansion of the portable fuel cell market is the development of hydrogen infrastructure. Governments are investing in the required infrastructure because they see hydrogen's potential as a clean energy carrier for fuel cells.
These expenditures cover the construction of hydrogen refueling stations as well as financing for facilities for the production, distribution, and storage of hydrogen. Governments can guarantee that fuel cell users have a dependable and practical source of hydrogen fuel by constructing a strong hydrogen infrastructure, which promotes broader adoption.
Public Procurement and Government Fleet Policies
Portable fuel cells are one of the clean energy solutions that many governments support with their purchasing power. Policies of government organizations may mandate that backup power systems or fuel cell-powered cars be taken into account for their fleets or facilities.
These regulations act as a showcase for fuel cell technology, showcasing its dependability and functionality in practical settings. Additionally, they open up a market for fuel cell producers, promoting innovation and competition in the industry.
In summary, the global market for portable fuel cells is significantly shaped by government regulations. Public procurement policies, tax incentives, RPS, research grants, environmental regulations, subsidies, and investments in hydrogen infrastructure all have an impact on the uptake and expansion of portable fuel cells. Governments' objectives to combat climate change, cut carbon emissions, and switch to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources are all in line with these policies.
Key Market Challenges
High Initial Cost and Limited Cost Competitiveness
The high initial cost of fuel cell systems in comparison to traditional power sources like internal combustion engines and batteries is one of the major obstacles facing the global portable fuel cell market. Complex manufacturing procedures are involved in portable fuel cell technologies, which frequently call for costly catalyst materials like platinum or other rare metals. Customers and companies interested in implementing fuel cell solutions must pay a higher upfront cost as a result.
Furthermore, the fuel cell industry has not yet fully benefited from economies of scale that have reduced the cost of many conventional power sources, such as lithium-ion batteries. Due to limited mass production and adoption, portable fuel cells have not been able to reach price competitiveness.
The market's expansion is hampered by this high initial cost, which presents a significant barrier to entry for many potential users. Government subsidies and incentives can help lessen this difficulty to some degree, but in order to make portable fuel cells a practical option for a wider range of industries and applications, production costs must be continuously reduced.
Efforts are ongoing to address this challenge through advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and economies of scale. The goal of research and development projects is to identify substitute catalyst materials, enhance production processes, and create novel fuel cell designs that can provide excellent performance at a reduced cost. It is anticipated that as these initiatives advance, portable fuel cells will become more cost-competitive, leading to a rise in market uptake.
Hydrogen Infrastructure Development
The growth and development of hydrogen infrastructure is a major obstacle facing the global portable fuel cell market. The availability of hydrogen refueling stations and distribution networks is essential for the broad use of portable fuel cells, particularly in applications like transportation, as hydrogen is a crucial fuel source for many fuel cell technologies.
A substantial investment in hydrogen production, storage, transportation, and refueling facilities is necessary to build a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure. These expenditures are necessary to guarantee that fuel cell users have a convenient and dependable source of hydrogen fuel, which is critical for market expansion.
Infrastructure for hydrogen has, however, developed more slowly than other clean energy sources. Regulatory approvals, safety standards, and coordination between different hydrogen supply chain stakeholders are among the challenges. To meet environmental objectives, hydrogen production techniques must also shift to more renewable and sustainable sources.
To overcome this obstacle, private sector investments and government assistance and incentives are crucial. Governments are offering financing and regulatory frameworks to hasten the development of hydrogen infrastructure as they become more aware of its significance. Governments, business leaders, and academic institutions must work together to overcome the logistical and technical obstacles related to the expansion of hydrogen infrastructure.
In conclusion, the development and growth of hydrogen infrastructure, as well as the high initial cost and low cost competitiveness of fuel cell systems, present challenges for the global portable fuel cell market. To overcome these obstacles and realize the full potential of portable fuel cell technology in a variety of applications, governments, businesses, and research institutions must continue their research, development, and cooperation efforts.
Segmental Insights
Diesel Insights
In 2022, the diesel segment held the largest market share, which it is anticipated to hold throughout the forecast period. Similar to conventional diesel engines, diesel fuel cells emit particulate matter and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These emissions can lead to air pollution and health issues, making them a serious environmental concern. Hydrogen fuel cells, on the other hand, only generate water vapor as a byproduct, which makes them a greener and cleaner choice. Because they convert a larger proportion of hydrogen's energy content into electrical power, hydrogen fuel cells are renowned for their high efficiency. Diesel engines, including those found in fuel cells, typically have lower efficiency, which results in increased energy losses and worse performance all around. In many portable and mobile applications, particularly in consumer electronics and lightweight devices, diesel engines—including those found in fuel cells—can generate noise and vibrations that are undesirable. In these situations, hydrogen fuel cells are frequently chosen because they are quieter and less likely to vibrate. Production, distribution, and refueling station infrastructure for hydrogen has grown more significantly, particularly in areas where clean energy and hydrogen economy projects are in progress. Conventional engines frequently use diesel, but fuel cells may not receive the same level of infrastructure support. Stricter environmental laws have been put in place in many nations and areas with the goal of lowering emissions and encouraging the use of cleaner energy sources. Hydrogen fuel cells are a better option for businesses and applications looking to adhere to environmental standards because they more closely match these regulations.
Automotive Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, the automotive segment is expected to grow rapidly over the course of the forecast period. The lack of infrastructure for hydrogen refueling prevented hydrogen FCVs from being widely adopted. Potential FCV users faced a major obstacle because hydrogen refueling stations were less prevalent than gas or electric vehicle charging stations. The convenience and accessibility of hydrogen-powered vehicles were restricted by this infrastructure gap, which slowed their adoption. Typically, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) needed costly parts, such as high-pressure hydrogen storage tanks and fuel cells. When compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles or electric vehicles, FCVs are less cost-competitive due to these components, which increased their manufacturing costs. Electric vehicles (EVs), which had become very popular in the automotive industry, posed a serious threat to hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). With a more advanced infrastructure for charging and cheaper battery production, EVs were viewed as a more dependable and affordable clean energy option. The acceptance and awareness of hydrogen FCVs among consumers were still developing. Many prospective buyers were more accustomed to gasoline or electric vehicles and felt apprehensive about the limited number of hydrogen refueling stations, despite the interest shown by some early adopters and environmentally conscious consumers in fuel cell vehicles. Regional differences existed in the degree of policy and regulatory support for hydrogen FCVs. While some regions prioritized EV incentives and infrastructure development, other regions, like Japan and parts of Europe, had more FCV-friendly policies and incentives.
Regional Insights
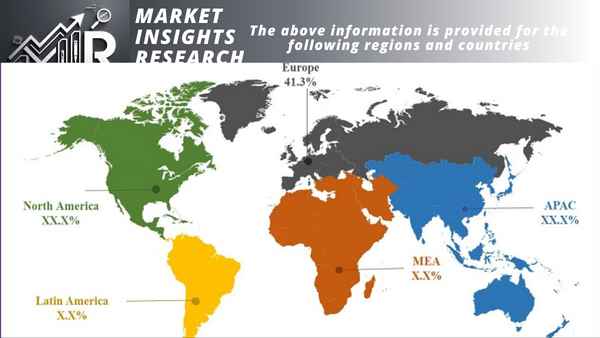
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region had the largest market for portable fuel cells, accounting for over 50% of the global market in 2022. The region is expected to continue to grow at a rapid pace in the coming years, driven by factors such as
Increasing demand for clean and sustainable energy sources
Government support for renewable energy and clean energy technologies
Rapid economic growth and urbanization
North America
The North American market for portable fuel cells had the second-largest market in the world, accounting for over 30% of the global market in 2022. The region is home to a number of leading manufacturers of portable fuel cells, as well as a growing number of companies that are developing new applications for portable fuel cells.
The North American market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by factors such as
Increasing demand for portable fuel cells in the consumer electronics and power tool markets
Government support for renewable energy and clean energy technologies
Growing adoption of portable fuel cells in the military and aerospace industries
Europe
The European market for portable fuel cells had the third-largest market in the world, accounting for over 15% of the global market in 2022. The region is home to a number of leading manufacturers of portable fuel cells, as well as a growing number of companies that are developing new applications for portable fuel cells.
The European market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by factors such as
Increasing demand for portable fuel cells in the consumer electronics and power tool markets
Government support for renewable energy and clean energy technologies
Growing adoption of portable fuel cells in the military and aerospace industries
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In January 2023, Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd. and Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power (KHNP) signed an agreement for strengthening Hydrogen Fuel Cell Operation and Maintenance Capabilities. The agreement includes a joint investment to develop new technologies and expand the use of portable fuel cells in South Korea.
- In February 2023, Renault Group and Plug Power Inc. entered into a joint venture with formation of HYVIA to work on low-carbon mobility and hydrogen fuel cells. The joint venture will invest USD320.80 million over the next five years to develop and commercialize new hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and technologies, including portable fuel cells.
- In March 2023, Ceres and HORIBA MIRA entered into a partnership for fuel cell testing and development of a Ceres fuel cell test facility at HORIBA MIRA West Midlands site in UK. The partnership will invest USD 10.69 million over the next three years to develop and test new portable fuel cell technologies.
Key Market Players
- Ballard Power Systems Inc
- Bloom Energy
- Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd
- Ceres Power Holdings plc
- Plug Power Inc
- Cummins Inc
- Altergy Systems
- SFC Energy AG
- FuelCell Energy Inc
- Watt Fuel Cell Corporation
|
By Fuel |
By End User |
By Type |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Residential Boiler Market Size By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil,...
- Commercial Electric Boiler Market - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), By Capacity, By Product (Hot Water,...
- Combi Boiler Market - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing) & Forecast, 2024-2032
Table of Content
- 1. Executive Summary
- 1.1. Key Findings
- 1.2. Market Overview (Global Fuel Cell Market size: ~$6.6 Billion in 2024, projected to reach ~$43.7 Billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 20.81% during 2025-2033; Portable segment is a subset)
- 1.3. Future Outlook and Growth Opportunities
- 2. Introduction to the Portable Fuel Cell Market
- 2.1. What are Portable Fuel Cells?
- 2.2. How Portable Fuel Cells Work (General Principles)
- 2.3. Types of Portable Fuel Cells Relevant to the Market
- 2.3.1. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
- 2.3.2. Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFCs)
- 2.3.3. Others (e.g., Alkaline Fuel Cells - AFCs)
- 2.4. Advantages of Portable Fuel Cells
- 2.4.1. Longer Runtime/Higher Energy Density than Conventional Batteries
- 2.4.2. Faster Refueling Times
- 2.4.3. Lightweight and Compact Design
- 2.4.4. Environmentally Friendly (Zero/Low Emissions)
- 2.4.5. Quiet Operation
- 2.4.6. Reliable Power Supply in Remote/Off-Grid Locations
- 2.5. Limitations of Portable Fuel Cells
- 2.6. Scope of the Report
- 3. Market Overview
- 3.1. Current Market Size and Valuation (2025, specific to Portable Fuel Cells if available, otherwise extrapolate from overall Fuel Cell market)
- 3.2. Market Dynamics
- 3.2.1. Drivers of Market Growth
- 3.2.1.1. Increasing Demand for Clean and Sustainable Energy Solutions
- 3.2.1.2. Growing Need for Reliable Power in Remote and Off-Grid Applications
- 3.2.1.3. Technological Advancements (Efficiency, Durability, Cost Reduction)
- 3.2.1.4. Expanding Applications in Consumer Electronics and Military/Defense
- 3.2.1.5. Expansion of Hydrogen Infrastructure (though less critical for some portable types like DMFC)
- 3.2.2. Challenges and Restraints
- 3.2.2.1. High Initial Costs Compared to Conventional Batteries
- 3.2.2.2. Challenges with Fuel Storage and Distribution (for hydrogen-based)
- 3.2.2.3. Competition from Evolving Battery Technologies (e.g., Lithium-ion)
- 3.2.2.4. Durability and Lifetime Concerns
- 3.2.1. Drivers of Market Growth
- 4. Market Segmentation
- 4.1. By Fuel Type
- 4.1.1. Hydrogen
- 4.1.2. Methanol
- 4.1.3. Other Fuels (e.g., Sodium Borohydride)
- 4.2. By Technology Type
- 4.2.1. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs)
- 4.2.2. Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFCs)
- 4.2.3. Other Portable Fuel Cell Technologies
- 4.3. By Application
- 4.3.1. Consumer Electronics (Laptops, Smartphones, Cameras)
- 4.3.2. Military and Defense (Field Operations, Communication Devices, UAVs)
- 4.3.3. Remote and Off-Grid Power (Telecom Towers, Weather Stations, Recreational Vehicles)
- 4.3.4. Emergency and Backup Power
- 4.3.5. Other Niche Applications (e.g., Medical Devices)
- 4.4. By Power Output (e.g., Watt-scale, Kilowatt-scale)
- 4.1. By Fuel Type
- 5. Regional Analysis
- 5.1. North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
- 5.2. Europe (Germany, UK, France, etc.)
- 5.3. Asia Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia)
- 5.3.1. High Demand from Consumer Electronics and Emerging Industrial Applications
- 5.3.2. Government Support for Fuel Cell Development
- 5.4. Latin America
- 5.5. Middle East & Africa
- 6. Competitive Landscape
- 6.1. Market Share Analysis of Key Players
- 6.2. Profiles of Major Companies in the Portable Fuel Cell Market
- 6.2.1. SFC Energy AG
- 6.2.2. Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies
- 6.2.3. Ballard Power Systems
- 6.2.4. Plug Power Inc.
- 6.2.5. Watt Fuel Cell Corporation
- 6.2.6. Adaptive Energy
- 6.2.7. Ultracell Corporation
- 6.2.8. Intelligent Energy (Focus on specific portable applications)
- 6.2.9. Doosan Mobility Innovation (for drone applications)
- 6.2.10. Other Prominent Players and Startups
- 6.3. Recent Developments, Partnerships, and Product Launches
- 6.4. Investment and Funding Trends
- 7. Technological Trends and Innovations
- 7.1. Miniaturization and Weight Reduction
- 7.2. Improvements in Fuel Cartridge Design and Energy Density
- 7.3. Enhanced Durability and Reliability for Rugged Applications
- 7.4. Development of Lower-Cost Materials and Manufacturing Processes
- 7.5. Integration with Other Power Sources (e.g., Hybrid Systems with Batteries)
- 8. Future Outlook and Projections (up to 2030/2035)
- 8.1. Forecasted Market Size and CAGR (specifically for the portable segment, if available)
- 8.2. Emerging Applications and Niche Markets
- 8.3. Impact of Policy Support and Hydrogen Economy Development
- 8.4. Strategic Recommendations for Market Players
- 9. Conclusion
Major Key Players & Manufacturers in the Portable Fuel Cell Market:
- Ballard Power Systems
- Plug Power Inc.
- SFC Energy AG
- Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies
- Intelligent Energy Limited
- W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.
- Johnson Matthey plc
- Bloom Energy
- FuelCell Energy, Inc.
- Nuvera Fuel Cells, LLC
- Panasonic Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation
- Cummins Inc.
- Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd.
- ITM Power PLC
- PowerCell Sweden AB
- Proton Motor Fuel Cell GmbH
- Ceres Power Holdings Plc
- ElringKlinger AG
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Fuji Electric Co. Ltd.
- Adaptive Energy
- Altergy Systems
- Adelan
- Special Power Sources
- ZTEK Corporation
- MICROrganic Technologies
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
