South Korea Fuel Cell Market
South Korea Fuel Cell Market By Type (Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC), Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC), Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC), Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC), Others), By Application (Portable, Stationary, Vehicle), By Size (Small and Large), By End User (Residential, Transportation, Data Center, Military & Defense, Others), By Region, Competition, Forecast and Opportunities 2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
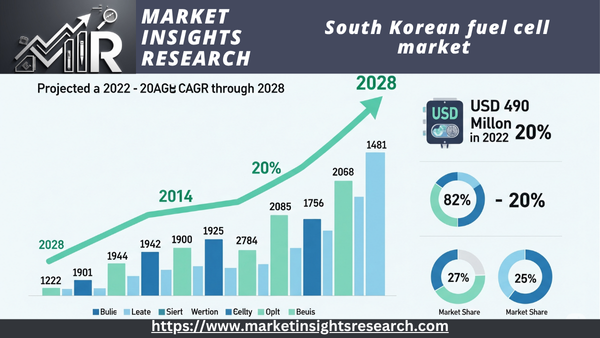
| Market Size (2022) | USD 490 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 20% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) |
| Largest Market | Northern |
Market Overview
With a 2022 valuation of USD 490 million, the South Korean fuel cell market is expected to develop at a phenomenal compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% through 2028. Because of their low emissions and effective energy generation, fuel cells—electrochemical devices that transform chemical energy into electrical power without combustion—have attracted a lot of attention.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Hydrogen and oxygen react under controlled conditions in a fuel cell, separating into protons and electrons. While electrons move through an external circuit to produce electricity, protons move through an electrolyte. Water is created and extra energy is released when the cathode interacts with oxygen. High efficiency, environmental friendliness, and silent operation are just a few of the many appealing benefits that fuel cells provide. They are used in a wide range of industries, from fuel cell automobiles and portable electronics to stationary power generation for residences and commercial buildings. Fuel cells are noteworthy for their substantial contribution to the advancement of sustainable energy solutions by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on fossil fuels.
The nation's commitment to sustainable development and inventive growth is reflected in the diverse factors propelling South Korea's booming fuel cell sector. One important element is the government's unwavering support and proactive measures. The government of South Korea has established a comprehensive system of rules, incentives, and funding mechanisms in recognition of the critical role that fuel cells play in guaranteeing energy security and sustainability. Comprehensive plans for developing fuel cell infrastructure and technologies include the Green New Deal and the Hydrogen Economy Roadmap. In addition to luring investments, generous subsidies, tax breaks, and research grants encourage industry participants to accelerate innovation and market penetration. This steadfast government support creates a strong basis for the thriving fuel cell industry in South Korea.
The South Korean fuel cell business is also being driven by the country's technological innovation capabilities. South Korea is renowned for its strong R&D skills and unwavering commitment to ongoing development. Fuel cell technology has advanced significantly as a result of these causes. Increased efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness are the outcomes of advancements in materials science, solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), and proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). In addition to encouraging domestic research, these technological developments position South Korea as a major player in the production and export of fuel cells worldwide. South Korean businesses are in a strong position to take advantage of the growing demand for renewable energy solutions worldwide.
Another strong argument in favor of fuel cells' broad use in a variety of South Korean industries is their adaptability. In addition to producing electricity, fuel cells are used in industrial processes, home energy systems, and transportation. Fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), aided by an expanding network of hydrogen filling stations, have been deployed as a result of South Korea's dedication to sustainable mobility. FCVs appeal to both consumers and enterprises because they provide emissions-free travel without range restrictions. Furthermore, fuel cells are incorporated into distributed energy systems and microgrids to provide dependable and clean power to consumers in the commercial, industrial, and residential sectors. This adaptability highlights how fuel cells have the ability to revolutionize many aspects of South Korea's economy and society.
Lastly, a collaborative culture enhances the fuel cell market in South Korea. It encourages collaborations between businesses, academic institutions, and foreign organizations. Participating in international consortia and actively participating in global renewable energy projects, South Korea promotes technology transfer, cross-border investments, and information exchange. By working together, South Korean businesses can increase their market reach, speed up innovation cycles, and get access to complementary resources and knowledge. Knowledge sharing, technological licensing contracts, and cooperative R&D projects all support a robust ecosystem that benefits from group advancement. By utilizing international collaborations, South Korea strengthens its position as a world leader in the fuel cell industry, increases its competitiveness, and speeds up commercialization.
In conclusion, a dynamic combination of government backing, technological advancements, a wide range of applications, and cooperative synergies is positioned to propel the South Korean fuel cell market toward extraordinary growth. Together, these motivating factors create an environment that is ideal for innovation, sustainable development, and revolutionary growth, solidifying South Korea's position as a leader in the world's shift to clean energy.
Supportive policies and Regulations are Likely to Propel the Market
The thriving and expanding fuel cell market in South Korea is largely due to a number of progressive and strong government regulations that offer a strong basis for business growth. In addition to demonstrating the government's dedication to sustainable development and clean energy, these regulations foster an atmosphere that encourages investment, innovation, and the broad use of fuel cell technology.
Hydrogen Economy Roadmap
The Hydrogen Economy Roadmap, a thorough and strategic framework outlining the country's objectives and concrete steps for the development of a hydrogen-based economy, is a pillar of South Korea's dedication to fuel cell innovation. The roadmap includes aggressive goals for technology advancement, infrastructural growth, and hydrogen generation. It provides a clear roadmap for developing a hydrogen ecosystem that includes sectors including power generation, transportation, and industrial operations. By demonstrating the government's sustained commitment to the fuel cell industry, this plan not only gives stakeholders a sense of direction but also inspires confidence in them. The Hydrogen Economy Roadmap guarantees a unified and well-aligned strategy to fuel cell development through fiscal assistance, regulatory incentives, and agency-to-agency collaboration.
Green New Deal Initiatives
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) for Hydrogen
Hydrogen is one of the renewable energy sources that the South Korean government has included in the Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS). Energy providers are required under this progressive policy to incorporate a specific proportion of hydrogen-based energy into their portfolios. The RPS policy essentially requires the integration of hydrogen-based technology, such as fuel cells, into the energy mix by designating hydrogen as a renewable source. This increases market demand and encourages infrastructural and production expenditures for hydrogen. The RPS policy demonstrates South Korea's goal of smoothly incorporating hydrogen into its energy mix, acting as a steady signal to the market for fuel cell adoption and spurring expansion along the value chain.
Research and Development (R&D) Funding and Collaboration
The South Korean government provides substantial financing for research and development initiatives in an effort to spur fuel cell innovation. Companies and research institutes are encouraged to work together on advanced fuel cell technology by the government through grants, subsidies, and tax advantages. These collaborations propel innovations in cost-effectiveness, durability, and efficiency, establishing South Korea as a global center for fuel cell research and development. In addition to promoting technical growth, the government's proactive support of R&D fosters a culture of cooperation and constant improvement, creating a strong ecosystem that benefits business, academia, and society as a whole.
In conclusion, a number of government-sponsored initiatives that create the conditions for long-term expansion, innovation, and broad fuel cell technology acceptance are the main reasons why South Korea's fuel cell sector is thriving. In addition to offering unambiguous direction and incentives, these policies demonstrate a strong dedication to utilizing fuel cells' potential as a catalyst for both environmental stewardship and economic growth.
Key Market Challenges
Although the fuel cell sector in South Korea is showing encouraging development and innovation, one of the main obstacles it must overcome is the difficult undertaking of quickly creating and expanding the infrastructure required to facilitate the broad use of fuel cell technology. The complexity of infrastructure development, which includes hydrogen production, distribution, refueling stations, and integration into other sectors, is the source of this difficulty.
Hydrogen Infrastructure Development
Building a strong and dependable infrastructure for hydrogen production is a crucial obstacle in South Korea's fuel cell path. An essential fuel for fuel cells, hydrogen necessitates effective production, storage, and delivery techniques. There are technological and logistical obstacles in creating a hydrogen supply chain that uses various sources, including natural gas, renewable energy, and electrolysis. To encourage the use of fuel cells in various industries, it is essential to guarantee a steady and sustainable supply of hydrogen at affordable prices.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Refueling Station Network
A robust network of hydrogen filling stations is necessary for fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) to emerge as a viable and appealing transportation option. Meeting the increasing demand for FCVs requires the prompt expansion of refueling infrastructure, which presents a difficulty. It takes significant planning and expenditure to strike a balance between the necessity of easy access to refueling stations and the profitability of station operations. In order to alleviate range anxiety and increase the viability of FCV ownership, it is imperative that refueling stations be available in both urban and rural locations.
In summary, the fuel cell market in South Korea faces the difficulty of quickly creating and expanding the complex infrastructure required to realize the full potential of fuel cell technology. Governments, business leaders, and academic institutions must work together to strategically handle the complexities of hydrogen production, delivery, refueling, and integration across several sectors in order to overcome this obstacle. By overcoming this obstacle, South Korea may establish itself as a world leader in the fuel cell industry and open the door to a creative and sustainable energy future.
Segmental Insights
Transportation
Fuel cells are essential to Indonesia's scientific advancement and economic growth. Fuel cell technology is emerging as a stimulus for innovation, job creation, and investment in high-tech businesses while the nation looks to improve its industrial and technological capacities. In this context, one of the main motivators is Indonesia's potential to evolve into a regional center for fuel cell manufacturing, research, and development. By making investments in research facilities, encouraging knowledge transfer, and fostering industry-academia partnerships, Indonesia can become a hub for fuel cell innovation. This promotes economic growth by drawing in both domestic and foreign investment, in addition to advancing technology. Additionally, there are chances for employment development along the value chain in the fuel cell business. Fuel cell-related activities create job opportunities for a qualified workforce, from research and development to production, installation, and maintenance. Through the provision of specialized skills and knowledge in advanced clean energy technology, this job generation aids in Indonesia's socioeconomic development. Fuel cells also provide a platform for promoting innovation in other fields. Advances in energy management, engineering, and materials research are required for developing fuel cell technology, which encourages interdisciplinary cooperation and knowledge sharing. These developments could spread to other industries, encouraging a technologically advanced society and solidifying Indonesia's standing as a leading innovator in the world. Indonesia can improve its technological capabilities, draw in investments, and create a knowledge-based economy by using fuel cell technology as a catalyst for innovation and economic growth. This factor not only puts Indonesia at the forefront of renewable energy solutions but also helps the country emerge as a major force in the world of innovation.
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
In 2022, the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) segment took the lead in the fuel cell market, and it is anticipated to continue to do so.
Regional Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, Gyeonggi Province is the top region in the North for the South Korean fuel cell market. This is due to the following factors
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government support
The government of Gyeonggi Province has made significant investments in infrastructure and research and development, and it has been a steadfast advocate for the fuel cell sector.
Availability of talent
Numerous universities and research facilities in Gyeonggi Province have been producing highly qualified personnel in the field of fuel cell technology.
Major companies
Many significant fuel cell companies, including Hyundai Motor Company, SK Innovation, and LG Chem, are based in Gyeonggi Province. These businesses are making significant investments in fuel cell research and development.
Recent Developments
- In February 2022, the South Korean government announced that it would invest USD 1.7 billion in the fuel cell industry over the next five years. The investment is aimed at developing new fuel cell technologies and expanding the use of fuel cells in transportation, stationary power, and portable power applications.
- In January 2022, the Hyundai Motor Company announced that it would invest USD 1 billion in the development of fuel cell vehicles over the next five years. The investment is aimed at increasing the production of fuel cell vehicles and expanding their sales in overseas markets.
- In December 2021, the SK Innovation company announced that it would invest USD 410 million in the development of fuel cell technologies over the next three years. The investment is aimed at developing new fuel cell technologies for transportation and stationary power applications.
- In November 2021, the LG Chem company announced that it would invest USD 170 million in the development of fuel cell technologies over the next two years. The investment is aimed at developing new fuel cell technologies for transportation and stationary power applications.
- In October 2021, the Doosan Fuel Cell company announced that it would invest USD 85 million in the development of fuel cell technologies over the next three years. The investment is aimed at developing new fuel cell technologies for transportation and stationary power applications.
- These are some of the recent investments in the fuel cell market in South Korea in 2022. The South Korean government and private companies are increasingly investing in fuel cell technology, as they see it as a key part of the future of clean energy.
Key Market Players
- Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd
- Hyundai Motor Company
- SK Innovation
- LG Chem
- Hyundai Rotem
- POSCO Energy
- Samsung SDI
- Hyundai Glovis
|
By Type |
By Application |
By Size |
By End User |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Residential Boiler Market Size By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil,...
- Commercial Electric Boiler Market - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), By Capacity, By Product (Hot Water,...
- Combi Boiler Market - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing) & Forecast, 2024-2032
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Overview
-
1.2 Key Developments and Forecast Highlights
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Scope and Objectives
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Fuel Cell Classifications
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 Fuel Cell Technology in the South Korean Energy Ecosystem
-
3.2 Role in the National Hydrogen Economy Plan
-
3.3 Evolution of South Korea’s Fuel Cell Industry
-
3.4 Strategic Importance in the Asia-Pacific Fuel Cell Market
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Market Drivers
-
4.1.1 Government Commitment to Hydrogen Economy 2.0
-
4.1.2 Deployment of Stationary Fuel Cells for Distributed Power
-
4.1.3 Commercialization of Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs)
-
-
4.2 Market Restraints
-
4.2.1 High System and Hydrogen Production Costs
-
4.2.2 Public Perception and Infrastructure Readiness
-
-
4.3 Market Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Export Potential of Fuel Cell Technologies
-
4.3.2 R&D Leadership in Solid Oxide and PEM Systems
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
-
5.2 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC)
-
5.3 Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC)
-
5.4 Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC)
-
5.5 Fuel Cell Components, Materials, and Hydrogen Infrastructure
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Fuel Cell Type
-
6.1.1 PEMFC
-
6.1.2 SOFC
-
6.1.3 Others
-
-
6.2 By Application
-
6.2.1 Transportation (Fuel Cell EVs, Buses, Trains)
-
6.2.2 Stationary Power (Residential, Industrial, Commercial)
-
6.2.3 Portable Power
-
-
6.3 By End-User
-
6.3.1 Automotive OEMs
-
6.3.2 Utilities and Energy Providers
-
6.3.3 Smart Cities and Government Projects
-
-
-
Regional Market Insights within South Korea
-
7.1 Seoul Capital Area (Urban and Smart Grid Projects)
-
7.2 Ulsan and Hydrogen Industry Clusters
-
7.3 Other Key Industrial and Technology Development Zones
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue and Installed Capacity Forecast
-
8.2 Fuel Cell Deployment by Sector and Region
-
8.3 Hydrogen Supply Chain Cost Outlook
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share of Key Players
-
9.2 Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 Doosan Fuel Cell
-
9.2.2 Hyundai Motor Group
-
9.2.3 POSCO Energy
-
9.2.4 SK E&S
-
9.2.5 Hanwha Solutions
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Research Ecosystem and University-Industry Partnerships
-
-
Policy and Regulatory Framework
-
10.1 South Korea’s Hydrogen Roadmap and Fuel Cell Targets
-
10.2 Fuel Cell Subsidy Programs and Incentives
-
10.3 Safety Codes, Transport Regulations, and International Cooperation
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 Fuel Cell Stack Cost Reduction Roadmap
-
11.2 Smart Fuel Cell Integration in Energy Communities
-
11.3 Global Leadership in Hydrogen Mobility and Export Markets
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 References and Data Sources
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
