Indonesia Fuel Cell Market
Indonesia Fuel Cell Market By Type (Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC), Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC), Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC), Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC), Others), By Application (Portable, Stationary, Vehicle), By Size (Small and Large), By End User (Residential, Transportation, Data Center, Military & Defense, Others), By Region, Competition, Forecast and Opportunities 2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
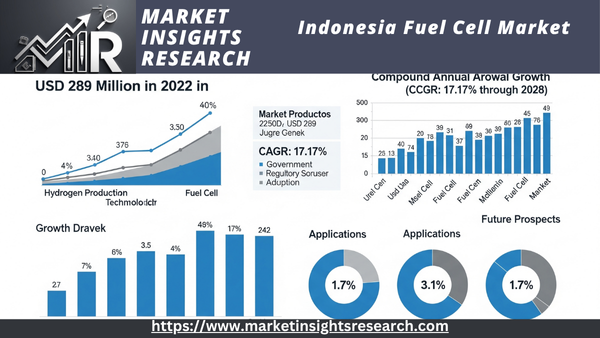
| Market Size (2022) | USD 289 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 17.17% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) |
| Largest Market | Java |
Market Overview
The Indonesia Fuel Cell Market, which was valued at USD 289 Million in 2022, is poised for substantial growth in the forecast period, displaying a robust CAGR of 17.17% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Introduction to Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are electrochemical devices that use a carefully regulated reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent to convert chemical energy from a fuel—typically hydrogen—into electrical energy. Fuel cells are an incredibly clean and efficient energy source because of its unique method, which avoids combustion and produces very little pollutants. Hydrogen molecules are converted into protons and electrons inside a fuel cell. An electric current is created when protons go through an electrolyte and electrons move through an external circuit. Oxygen works with protons and electrons at the cathode to create water while releasing more energy. Among the many benefits of fuel cells are their high efficiency, low environmental impact, and quiet operation. They are used in a variety of fields, such as portable electronics, transportation (including fuel cell vehicles), and stationary power generation for homes and businesses. Fuel cells are essential for lowering greenhouse gas emissions and lowering reliance on fossil fuels, which advances sustainable energy solutions in a variety of industries.
Key Market Drivers
Diversification of Energy Sources and Clean Energy Goals
The need to diversify its energy sources and meet aggressive clean energy targets is driving the fuel cell market in Indonesia. As a fast-growing country with significant and rising energy consumption, Indonesia understands the importance of reducing dependency on fossil fuels and shifting to more ecologically friendly and sustainable energy sources. The government's steadfast dedication to increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy grid is a key motivator in this regard.
Indonesia has set aggressive goals to produce a significant amount of its energy from renewable sources, including fuel cell technology and hydrogen-based technologies. This dedication is supported by the country's abundant renewable resources, including biomass, wind, and sun, which may be used to produce hydrogen and power fuel cells. Indonesia can diversify its energy sources and help create a greener, more resilient energy future by adopting fuel cells. Fuel cells offer a flexible solution that can provide clean and reliable power for a variety of uses, such as transportation, off-grid energy access, and electricity generation. Fuel cells are positioned as a crucial enabler of Indonesia's path towards sustainable development due to their smooth alignment with the country's clean energy objectives.
Additionally, by reducing its reliance on imported fossil fuels, the use of fuel cells can strengthen Indonesia's energy security. With the development of fuel cell technology and the expansion of domestic hydrogen production capacity, the country can achieve greater energy independence and reduce the dangers associated with unstable international energy markets. Fuel cells are a tempting option for Indonesia's energy landscape because of this push for energy security and diversification, which promotes both environmental stewardship and economic growth.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Urbanization and Sustainable Mobility Solutions
The need for sustainable mobility solutions is urgent due to Indonesia's cities' rapid urbanization and population increase, which makes the fuel cell market a key force behind advancement. Fuel cells provide a revolutionary solution that is in line with the nation's urban development goals, as metropolitan areas struggle with air pollution, traffic congestion, and the need for dependable transportation. The potential of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) to completely transform the transportation industry is a key factor propelling Indonesia's fuel cell market. FCVs offer a compelling substitute for traditional internal combustion engine vehicles as cities work to lower emissions and improve air quality. Fuel cells contribute to cleaner air and healthier urban environments by providing zero-emission mobility, with the sole result being water vapor. The government's promotion of electric vehicles and the construction of charging infrastructure serve to further solidify Indonesia's commitment to sustainable mobility. Fuel cell vehicles offer a potential remedy for the range anxiety and charging issues related to electric mobility because of their wider driving ranges and quicker refilling periods when compared to battery electric vehicles. Fuel cell technology has potential for usage in delivery trucks, buses, taxis, and other urban mobility alternatives in addition to passenger cars. This wide range of possible uses highlights how fuel cells will influence Indonesia's urban transportation system in the future. In addition to lowering pollution and urban congestion, Indonesia may further its clean energy transition by utilizing fuel cell technology to meet the demands of sustainable mobility. The rise in fuel cell-powered automobiles supports the nation's urban development objectives and makes cities more livable, efficient, and sustainable.
Economic Development and Technological Innovation
In Indonesia, fuel cells are essential for both scientific advancement and economic growth. Fuel cell technology is emerging as a stimulus for innovation, job creation, and investment in high-tech businesses as the nation looks to improve its industrial and technological capabilities. The potential for Indonesia to emerge into a regional center for fuel cell manufacturing, research, and development is one of the main motivators in this regard. Indonesia should position itself as a hub for fuel cell innovation by funding research institutes, encouraging technology transfer, and fostering academic-industry partnerships. By drawing in both domestic and foreign investment, this promotes economic growth in addition to advancing technology. Additionally, the market for fuel cells offers chances to create jobs along the whole value chain. Jobs for a skilled workforce are created by fuel cell-related operations, which range from research and development to production, installation, and maintenance. By providing its workers with specialized knowledge and skills in cutting-edge renewable energy technology, this employment generation aids in Indonesia's socioeconomic development. Additionally, fuel cells offer a platform for promoting innovation in other fields. Advances in materials science, engineering, and energy management are necessary for the development of fuel cell technology, which encourages interdisciplinary cooperation and knowledge sharing. These developments could spread to other sectors of the economy, encouraging a culture of technological innovation and solidifying Indonesia's standing as a world leader in innovation. By adopting fuel cell technology as a catalyst for innovation and economic growth, Indonesia can advance its technological capabilities, draw in foreign capital, and provide the foundation for a knowledge-based economy. In addition to placing Indonesia at the forefront of sustainable energy solutions, this driver helps the country emerge as a competitive force in the global innovation arena.
Supportive policies and Regulations are Likely to Propel the Market
National Hydrogen Roadmap and Investment Incentives for Fuel Cells
In order to boost the fuel cell market's expansion, the Indonesian government has established a thorough National Hydrogen Roadmap in recognition of the technology's revolutionary potential. The development, application, and integration of hydrogen-based technologies, such as fuel cells, across several economic sectors are outlined in this policy framework. A variety of investment incentives aimed at stimulating private sector involvement and innovation in the fuel cell business form the foundation of this supporting strategy. For companies and groups involved in fuel cell research, development, manufacture, and commercialization, the government provides funding possibilities, tax breaks, and targeted financial subsidies. These incentives encourage stakeholders to engage in fuel cell technology, spur breakthroughs, and establish a thriving ecosystem for sustainable energy solutions in addition to easing capital limitations. Additionally, the National Hydrogen Roadmap makes it easier for government organizations, business leaders, and academic institutions to work together on fuel cell initiatives. By fostering knowledge sharing, expediting the permitting process, and establishing a favorable regulatory environment, the government acts as a facilitator. By working together, fuel cell solutions are developed and adopted more quickly, creating a vibrant ecosystem that promotes economic growth and innovation. The policy's dedication to building a hydrogen infrastructure, which includes networks for hydrogen generation, storage, and delivery, is another essential component. A consistent supply of hydrogen, which is essential for fuel cell functioning, is made available by the government's support of infrastructural development. Because of this dedication, companies may invest in fuel cell technology with confidence that hydrogen fuel will be available. In conclusion, a strong and comprehensive governmental approach to fostering Indonesia's fuel cell market is represented by the National Hydrogen Roadmap and the investment incentives that go along with it. This policy framework places Indonesia as a leader in the worldwide shift to clean energy technologies by facilitating the widespread adoption of fuel cells through the combination of financial incentives, cooperative partnerships, and infrastructure development.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Research and Innovation Grants for Fuel Cell Advancements
Key Market Challenges
Infrastructure Development and Hydrogen Supply Chain Challenges in Indonesia's Fuel Cell Market
Although the fuel cell market in Indonesia has a lot of potential, building a strong hydrogen infrastructure and a trustworthy supply chain would be a major obstacle. The availability of hydrogen, a vital fuel supply for fuel cells, is essential to the successful integration of fuel cell technology. But creating a complete hydrogen supply chain—which includes production, distribution, storage, and transportation—presents challenging obstacles that call for cooperation and strategic planning. The creation of hydrogen is one of the main obstacles. Although Indonesia has a wealth of renewable resources, like solar and wind energy, that can be used to produce hydrogen, the shift to large-scale, economically viable hydrogen production techniques is still a difficult undertaking. Technologies like electrolysis, which uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, must be scaled up with a large infrastructure investment and cost-effectiveness and efficiency improvement. Furthermore, resolving storage and transportation issues is essential to guaranteeing a consistent supply of hydrogen. Because of its particular storage needs, hydrogen requires specialized infrastructure to be transported and stored properly. Long-distance or remote hydrogen transportation necessitates the construction of pipelines, compression stations, or alternative storage options, which complicates the supply chain. Building a network of hydrogen refueling stations is essential to overcoming this obstacle. Similar to conventional petrol stations, fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) need an easy-to-access refueling infrastructure to be widely used. Land purchase, technical requirements, regulatory permissions, and a substantial financial investment are all necessary to establish a network of hydrogen refueling stations throughout cities, roads, and rural areas. Furthermore, resolving these infrastructure issues requires coordination between numerous stakeholders. Government agencies, energy firms, academic institutions, and private businesses must work together to share knowledge, pool resources, and expedite regulatory procedures. The development of the required supply chain and infrastructural components can be accelerated through efficient coordination and interest alignment. Indonesia needs to take a comprehensive approach that includes public-private partnerships, regulatory assistance, and technological innovation in order to overcome these obstacles. Targeted incentives for the generation of hydrogen and the development of infrastructure, in conjunction with strategic investments in research and development, can spur the development of hydrogen technologies and drive the growth of the fuel cell market. Indonesia can realize the full potential of fuel cell technology, support sustainable energy goals, and establish itself as a leader in the worldwide shift to clean energy solutions by tackling supply chain and infrastructure issues.
Segmental Insights
Transportation
In 2022, the transportation segment took the lead in the fuel cell market, and it is anticipated to stay that way for the duration of the forecast. Air pollution and traffic congestion are major problems in Indonesia's heavily populated urban areas. Fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are a game-changing option that fits in with the government's objectives for urban development. Because FCVs only generate water vapor and have no tailpipe emissions, they help to improve air quality and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Traffic congestion can be greatly reduced and urban life can be improved by the use of FCVs for ride-sharing, taxis, and public transportation. Due to its large size, Indonesia has particular transportation needs, particularly when it comes to distant areas and expansive islands. By providing longer driving ranges and quick refueling, fuel cells solve the problem of long-range connection and get around the drawbacks of battery electric vehicles. Fuel cell-equipped FCVs are ideal for intercity travel since they allow for smooth and environmentally friendly transit over a variety of terrains. Conventional energy infrastructure is not available in many areas of Indonesia. For off-grid locations, fuel cell technology can offer a dependable and sustainable energy source, facilitating movement in areas with little to no access to conventional fuel sources. In isolated and underprivileged areas, fuel cell-powered cars, boats, and even two-wheelers can improve transportation and boost the local economy.
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
In 2022, the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) segment took the lead in the fuel cell market, and it is anticipated to continue to do so.
Regional Insights
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In July 2022, the Indonesian government announced that it would invest USD 1 billion in a new hydrogen production and distribution network. The network is expected to be completed by 2025 and will help to support the development of the fuel cell market.
- In June 2022, the Hyundai Motor Company announced that it would invest USD 100 million in a new fuel cell research and development facility in Indonesia. The facility is expected to create 100 new jobs and will focus on developing new fuel cell technologies for vehicles and stationary applications.
- In May 2022, the Pertamina Energy Research Institute (PEI) announced that it would collaborate with the National University of Singapore to develop a new type of fuel cell. The fuel cell is expected to be more efficient and cost-effective than current technologies.
- In April 2022, the Toyota Motor Corporation announced that it would invest USD 50 million in a new fuel cell production plant in Indonesia. The plant is expected to be completed by 2024 and will produce fuel cells for Toyota's hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
- In March 2022, the Air Liquide company announced that it would invest USD 20 million in a new hydrogen refueling station in Indonesia. The station is expected to be operational by the end of 2023 and will be the first of its kind in Indonesia.
Key Market Players
- PT HyET Hydrogen Indonesia
- PT Aneka Gas Industrie
- PT PLN (Persero)
- PT Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indonesia
- PT Astra International Tbk
- PT Hyundai Motor Manufacturing Indonesia
|
By Type |
By Application |
By Size |
By End User |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Residential Electric Boiler Market Size - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), Industry Analysis Report, Reg...
- Europe Steam Boiler Market - By Capacity, By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), ...
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Residential Boiler Market Size By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil,...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Snapshot
-
1.2 Key Trends and Strategic Highlights
-
1.3 Growth Forecast and Policy Opportunities
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Objectives and Scope
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Classification
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What Are Fuel Cells?
-
3.2 Indonesia’s Energy Landscape and Role of Fuel Cells
-
3.3 Comparison with Batteries and Diesel Generators
-
3.4 Market Potential within Renewable and Off-Grid Systems
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Market Drivers
-
4.1.1 Push for Decentralized and Off-Grid Power Access
-
4.1.2 Integration with National Renewable Energy Roadmap
-
4.1.3 Rising Industrial and Telecom Backup Demand
-
-
4.2 Market Restraints
-
4.2.1 High Initial Cost and Lack of Local Manufacturing
-
4.2.2 Limited Hydrogen Infrastructure and Public Awareness
-
-
4.3 Market Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Fuel Cells for Island Electrification and Mining Sites
-
4.3.2 International Partnerships and Technology Transfer
-
-
4.4 Market Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC)
-
5.2 Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)
-
5.3 Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFC)
-
5.4 Methanol and Biogas Fuel Cell Applications in Indonesia
-
5.5 Hydrogen Generation and Storage Readiness
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Fuel Cell Type
-
6.1.1 PEMFC
-
6.1.2 SOFC
-
6.1.3 Others
-
-
6.2 By Application
-
6.2.1 Power Backup for Telecom and Industrial Sites
-
6.2.2 Renewable Integration and Microgrids
-
6.2.3 Mobility and Off-Road Vehicles (Future Potential)
-
-
6.3 By End-User
-
6.3.1 Utilities and Government Projects
-
6.3.2 Mining and Resource Sector
-
6.3.3 Commercial and Telecom
-
6.3.4 Others
-
-
-
Regional Opportunity Zones in Indonesia
-
7.1 Java and Bali (Urban Backup and Industrial Sites)
-
7.2 Sumatra and Kalimantan (Remote Power Access)
-
7.3 Sulawesi, Papua, and Eastern Islands (Island Electrification)
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue Forecast by Region and Application
-
8.2 Installed Base and Deployment Growth Potential
-
8.3 Cost Trends and Localization Scenarios
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Mapping of International Entrants and Local Stakeholders
-
9.2 Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies
-
9.2.2 Toshiba Energy Systems
-
9.2.3 Ballard Power Systems
-
9.2.4 Local EPC and Pilot Partners
-
-
9.3 Recent Pilots, Demonstrations, and Public-Private Initiatives
-
-
Policy and Regulatory Framework
-
10.1 National Energy Policy and Hydrogen Roadmap
-
10.2 Incentives for Renewable and Fuel Cell Integration
-
10.3 Import Regulations, Safety, and Certification Standards
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 Fuel Cells in Off-Grid Electrification Programs
-
11.2 Green Hydrogen Collaboration with ASEAN and International Agencies
-
11.3 Potential for Fuel Cells in Maritime and Rail Applications
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 References and Sources
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
