Industrial Lead Acid Battery Market
Industrial Lead Acid Battery Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Product (Stationary, Motive, and Start Light & Ignition Batteries (SLI)), By Construction Method (Flooded and Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) Batteries), By Sales Channel (Original Equipment Market (OEM) & Aftermarket) By Region, Competition, 2018-2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
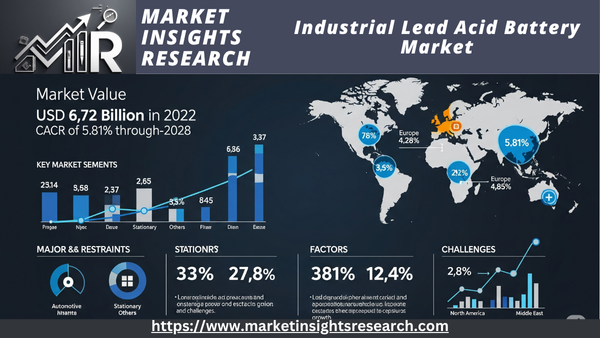
| Market Size (2022) | USD 6.72 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 5.81% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Start Light & Ignition Batteries (SLI) |
| Largest Market | Asia-Pacific |
Market Overview
Global Industrial Lead Acid Battery Market was valued at USD 6.72 Billion in 2022 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of 5.81% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Key Market Drivers
Expanding Telecommunications Infrastructure
The growing telecommunications infrastructure is one of the main factors propelling the industrial lead-acid battery market. In order to guarantee continuous operation, telecommunications networks mostly depend on backup power solutions, particularly in regions that frequently experience power outages or lack dependable grid connections. In the telecommunications sector, lead-acid batteries have long been used for backup power because of their proven dependability, affordability, and capacity to deliver energy when it's most required. During blackouts, these batteries provide a reliable power source, guaranteeing that communication networks continue to function. The need for industrial lead-acid batteries in the telecommunications industry is only increasing due to the continuous development of mobile networks, the spread of data centers, and the development of rural connectivity projects. This driver stimulates technological developments targeted at enhancing battery performance and lifespan by creating a steady market for suppliers and manufacturers. Additionally, the telecom sector is adopting lead-acid batteries for energy storage applications due to developments in hybrid power systems and renewable energy integration. The market is expanding and innovating as a result of this trend towards sustainable and green solutions.
Growth in Data Centers and Cloud Computing
The market for industrial lead-acid batteries is also significantly influenced by the quick growth of data centers and the increasing importance of cloud computing services. Because they store and analyze enormous volumes of data for consumers, governments, and enterprises, data centers are crucial parts of the digital age. To protect important data and guarantee smooth operations, data centers need dependable and uninterruptible power sources. Because of its high energy density and resistance to frequent charge-discharge cycles, lead-acid batteries are the recommended option for backup power in data centers. The need for industrial lead-acid batteries as a dependable backup power source is growing as more companies invest in hyperscale data centers and move their IT operations to the cloud. Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems use these batteries to fill the void left by power outages until alternate power sources, such generators, are turned on. Operators of data centers are also looking into ways to minimize their environmental impact and improve energy use. Lead-acid battery technologies have advanced as a result of this trend, including sophisticated VRLA (Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid) batteries that provide increased efficiency and lower maintenance needs. In conclusion, the market for industrial lead-acid batteries is significantly influenced by the expansion of data centers and cloud computing services. These batteries are essential in the digital age because they guarantee data integrity and business continuity. The market is growing and changing as a result of the continuous development of data center infrastructure and the search for energy-efficient solutions.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Robust Demand from Automotive and Transportation Sector
Vehicles have traditionally been powered by lead-acid batteries, especially in the automotive and transportation industries. Lead-acid batteries are still a common option for internal combustion engine vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and auxiliary systems, even if lithium-ion batteries have become more prevalent in EVs. These batteries are used in cars to power different electronics, light up the interior, and start the engine. Lead-acid batteries are also widely used in commercial vehicles, including trucks, buses, and heavy machinery, where dependability and affordability are important considerations. Additionally, train systems, aircraft ground support equipment, and marine vessels all employ industrial lead-acid batteries. The need for long-lasting and effective energy solutions in automobiles and other applications will continue to fuel the expansion of the industrial lead-acid battery market as the global transportation sector develops.
Industrial Growth and Infrastructure Development in Emerging Markets
The market for industrial lead-acid batteries is mostly driven by the fast industrialization and infrastructure growth in emerging regions. The need for dependable power solutions rises as these economies see an increase in urbanization and the growth of their manufacturing sectors. In areas with unstable grid infrastructure, industries including mining, data centers, telecommunications, and construction mainly depend on backup power to continue operating. In underdeveloped nations, where building a strong and dependable power infrastructure can be difficult, industrial lead-acid batteries provide an affordable way to meet energy demands. By filling the gap between sporadic power supplies and steady energy requirements, these batteries guarantee uninterrupted operations and minimize losses. In emerging countries, there is a significant need for industrial lead-acid batteries to support infrastructure expansion and improve operational reliability due to the expanding industrialization and urbanization of these regions.
Heavy Machinery and Equipment Applications
Heavy machinery and equipment are among the many industrial applications that heavily rely on lead-acid batteries. These batteries give construction equipment, mining machinery, agricultural vehicles, and material handling equipment the electricity they need to start engines, run hydraulic systems, and power onboard electronics. Reliable power sources are crucial for ensuring smooth operation and productivity in industries where heavy gear serves as the foundation of operations. Because of their strength, resilience to adverse environments, and ability to produce large current outputs, lead-acid batteries are well-suited for demanding applications. Industrial lead-acid batteries are still in high demand since heavy gear is still necessary for industries to run efficiently.
Research and Development in Battery Technologies
Continuous research and development initiatives to enhance battery longevity, performance, and environmental sustainability are advantageous to the industrial lead-acid battery market. To increase the overall effectiveness and longevity of lead-acid batteries, manufacturers are spending money on technologies including better electrolytes, innovative materials, and improved electrode designs. Developing recycling technology and improving battery designs for higher energy density and longer cycle life are two ways to reduce the environmental impact of lead-acid batteries. Because of these developments, lead-acid batteries are now more appealing to businesses looking for green energy options. The market for industrial lead-acid batteries is expanding due to the combination of market demand for sustainable, effective energy storage solutions and advancements driven by research.
In conclusion, a number of reasons, such as the requirement for a steady power supply, the integration of renewable energy, a variety of industrial applications, the growth of infrastructure, and continuous developments, are driving the market for industrial lead-acid batteries. Since lead-acid batteries continue to be a dependable and adaptable energy storage option for a range of industrial industries, these factors taken together support the market's growth.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government Policies are Likely to Propel the Market
Environmental Regulations and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental laws have been put in place by governments all around the world to control the manufacture, use, and disposal of lead-acid batteries. The goal of these regulations is to reduce the negative effects that lead, sulfuric acid, and other materials used in battery production have on the environment. Among these regulations' salient features are
Recycling RequirementsA lot of nations mandate that battery manufacturers set up and finance recycling initiatives. These initiatives guarantee the environmentally appropriate collection, transportation, and recycling of spent lead-acid batteries. Recycling lessens the environmental impact of battery production by recovering important components like lead and plastic.
Pollution ControlTo safeguard the quality of the air and water, governments impose restrictions on lead and sulfuric acid emissions from battery production sites. Strict emissions regulations and monitoring systems are in place to stop pollution and the harm it does to the environment and public health.
Battery Labeling and DisposalGovernments frequently require unambiguous labeling and recommendations to educate businesses and consumers about how to handle and dispose of lead-acid batteries. To avoid contaminating the environment, this includes guidelines for recycling and proper disposal techniques.
Energy Storage Incentives and Subsidies
Governments may provide incentives and subsidies to stimulate the use of lead-acid batteries in a variety of applications and to promote energy storage technologies. Businesses and industries wishing to invest in energy storage systems for grid stabilization, backup power, and renewable energy integration are supported by these rules. Among these incentives' salient features are
Tax CreditsBusinesses and homeowners who purchase energy storage systems that employ lead-acid batteries may be eligible for tax credits or deductions from their governments. The upfront expenses of putting battery-based energy solutions into place are partially covered by these financial incentives.
Grants and SubsidiesEnergy storage-focused organizations and projects are eligible for grants and subsidies, especially in areas like off-grid electrification, grid modernization, and renewable energy integration. Some of the expenses related to installing lead-acid batteries may be covered by these funds.
Feed-in tariffs and net meteringIn certain areas, businesses or individuals are able to sell excess energy stored in lead-acid batteries back to the grid through feed-in tariffs or net metering. Energy storage becomes more financially attractive as a result of these measures, which give battery owners new sources of income.
Safety Standards and Certification Requirements
To guarantee public safety and product dependability, governments set safety regulations and certification standards for the production, installation, and upkeep of lead-acid batteries. These guidelines cover topics like battery performance, design, labeling, and installation techniques. Important facets of safety rules consist of
Product CertificationBefore being put on the market, lead-acid batteries must pass stringent safety and performance requirements and be put through a rigorous testing process by accredited certification organizations. Batteries that have been certified are safe to use in a variety of applications.
Guidelines for Installation and MaintenanceTo ensure that lead-acid battery systems are installed and maintained correctly, governments may establish rules and guidelines. These regulations aid in preventing mishaps, fires, and other safety risks brought on by inappropriate handling.
Labeling and DocumentationIn order to educate end users on safe handling, maintenance, and disposal procedures, manufacturers are frequently obliged to provide thorough documentation and labeling on batteries. These recommendations help ensure that lead-acid battery systems operate safely.
Trade and Import Policies
The market for industrial lead-acid batteries may be impacted by trade and import regulations that governments enact. To manage the import and export of lead-acid batteries, these regulations may involve import quotas, tariffs, and quality control procedures. Important facets of trade policies consist of
Tariffs and DutiesTo safeguard domestic producers or raise money, governments may apply import taxes or tariffs on lead-acid batteries. The cost and competitiveness of imported batteries may be impacted by these taxes.
Import QuotasIn order to maintain a balanced market, some nations impose restrictions on the amount of lead-acid batteries that can be imported. These quotas are frequently employed to regulate the dynamics of supply and demand.
Quality Control and CertificationGovernments may mandate that imported goods go through certification or testing prior to being on sale in order to guarantee that imported lead-acid batteries fulfill safety and quality requirements. This guarantees that customers can obtain dependable and secure items.
Research and Development Incentives
Governments may provide research and development (R&D) incentives to promote battery technology innovation and the creation of sophisticated lead-acid batteries. In order to spur improvements in battery performance and efficiency, these incentives are intended to encourage cooperation between the commercial sector, academic institutions, and research centers. Important facets of R&D incentives consist of
Grants & FundingGovernments support groups and initiatives devoted to lead-acid battery research and development financially through grants, subsidies, and funding programs. Prototyping, testing, and innovation initiatives can be supported with these monies.
Tax BenefitsBusinesses involved in battery research and development are eligible for tax incentives, such as R&D tax credits. These tax advantages promote investment in technological developments and lower the overall cost of research.
Collaborative InitiativesTo encourage cooperative R&D efforts, governments may help establish alliances between universities, research centers, and battery manufacturers. These programs encourage the sharing of information and the development of new technologies.
Environmental Impact Assessments and Permits
Businesses frequently need to complete environmental impact studies (EIAs) and secure permits from the appropriate government agencies prior to setting up lead-acid battery production or recycling plants. These regulations are intended to assess and control the effects that battery manufacturing and recycling have on the environment. Important features of permits and EIAs include
Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) are thorough investigations that evaluate the potential effects of lead-acid battery production or recycling activities on the environment, including the air, water, soil, and nearby ecosystems. The evaluations aid in locating possible hazards and countermeasures.
Permitting ProcedureBusinesses need to get permits from regulatory bodies in order to run a battery production or recycling operation. To reduce adverse effects, these permits include particular requirements, guidelines, and environmental protections that must be adhered to.
Monitoring and ComplianceGovernments keep an eye on and enforce adherence to environmental laws and permit requirements. Lead-acid battery plants are guaranteed to follow environmental regulations and take the required precautions to preserve the environment through routine inspections and reporting requirements.
In summary, the market for industrial lead-acid batteries is greatly influenced by government policies that address environmental issues, encourage safety, fund research and development, control trade, provide incentives for energy storage, and set quality standards. For lead-acid batteries to grow sustainably and be used responsibly across a range of sectors and applications, these regulations are essential.
Key Market Challenges
Environmental Concerns and Lead-Acid Battery Recycling Challenges
Environmental Issues
The serious environmental issues surrounding lead-acid batteries are one of the biggest obstacles facing the industrial lead-acid battery business. The use of lead, sulfuric acid, and other potentially dangerous substances in the production and recycling of lead-acid batteries is the main source of these worries.
Exposure to LeadLead is a hazardous heavy metal that can have a major negative impact on both human and environmental health. Lead poisoning, which can impact the kidneys, neurological system, and other essential systems, can result from prolonged exposure to lead. Pregnant women and children are more susceptible to lead exposure.
Acidic ElectrolyteThe electrolyte of lead-acid batteries is sulfuric acid, which is extremely corrosive and dangerous for the environment if not handled and disposed of appropriately. Unintentional sulfuric acid spills or leaks can damage wildlife, waterways, and land.
Challenges with Recycling
Recycling is a vital component of the lead-acid battery business to help alleviate these environmental issues. Recycling lead-acid batteries lessens the environmental impact of battery manufacturing while recovering valuable components including lead, plastic, and sulfuric acid. However, recycling lead-acid batteries presents a number of difficulties
a. Informal RecyclingThere are unregulated, informal lead-acid battery recycling businesses in some areas, which frequently lack the necessary environmental controls and safety precautions. Lead and sulfuric acid may be released into the environment as a result, endangering the health of the ecosystems and communities nearby.
b. Infrastructure and ComplianceSetting up effective and ecologically conscious recycling infrastructure is expensive and necessitates following stringent environmental laws. Existing and new recycling plants may find it difficult to meet these regulatory criteria.
c. Collection and TransportationIt might be logistically difficult to gather spent lead-acid batteries from different locations and deliver them to recycling facilities. It's crucial to make sure spent batteries are handled carefully and transported without spilling or leaking.
For the industrial lead-acid battery business to grow sustainably, these environmental issues and recycling difficulties must be resolved. To enforce stringent laws, encourage appropriate recycling methods, and make investments in cleaner and more ecologically friendly battery technology, governments and industry partners must work together.
Competition from Alternative Battery Technologies
Alternative battery technologies, especially lithium-ion batteries and new innovative energy storage solutions, are becoming a bigger threat to the industrial lead-acid battery business. These substitutes have a number of benefits over conventional lead-acid batteries, and the lead-acid battery industry is facing serious competition as a result of their increasing use.
Alternative Battery Technologies' Benefits
A number of benefits make lithium-ion batteries and other cutting-edge energy storage technologies appealing to both commercial and industrial uses.
Energy DensityThe energy density of lithium-ion batteries is higher than that of lead-acid batteries. This makes them appropriate for applications with limited space since they can store more energy in a lighter and smaller container.
Extended Cycle LifeIn general, lithium-ion batteries outlast lead-acid batteries in terms of cycle life. For applications requiring endurance and durability, their capacity to tolerate a greater number of charge-discharge cycles without experiencing appreciable degradation is essential.
Rapid ChargingBecause lithium-ion batteries can charge more quickly, they can respond to grid balancing or backup power demands more quickly.
Reduced Self-DischargeBecause lithium-ion batteries have reduced rates of self-discharge, they can hold onto stored energy for extended periods of time without suffering appreciable losses.
New TechnologiesIn addition, new energy storage technologies like solid-state and flow batteries provide special benefits in terms of environmental impact, safety, and scalability. Research and development on these technologies is ongoing, and they could eventually compete with lead-acid batteries.
Challenges for the Lead-Acid Battery Market
The market for lead-acid batteries faces a number of difficulties as a result of competition from these other battery technologies
Market Share ErosionAs alternative technologies become more popular, lead-acid batteries' market share is being reduced, especially in applications where cutting-edge performance and features are valued highly.
Research and DevelopmentIn order to stay competitive, lead-acid battery producers must make investments in R&D to improve the functionality, effectiveness, and environmental sustainability of their products.
Lead-acid battery prices are under pressure as a result of economies of scale and technological developments that make lithium-ion batteries and other substitutes more affordable.
Adoption ObstaclesBusinesses and industries used to lead-acid batteries may find it difficult to overcome the inertia involved in implementing new technology. It could be necessary to make educational efforts to highlight the advantages of more recent options.
Segmental Insights
Start Light & Ignition Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, the Start Light & Ignition category is anticipated to hold a dominant position throughout the projected period. One subset of the industrial lead-acid battery industry is Light & Ignition Batteries, also known as automobile batteries. These batteries are intended to supply the first surge of power needed to start the engines of automobiles, trucks, motorcycles, and other vehicles powered by internal combustion engines. In order to turn over the engine's starter motor, light and ignition batteries are designed to provide a large amount of cranking power in a brief burst. These batteries are recharged by the car's alternator while the engine is operating. The global automobile sector is the main source of demand for light and ignition batteries. The need for automotive batteries is growing along with the number of automobiles on the road. This covers not just automobiles and motorbikes but also trucks, heavy equipment, and commercial vehicles that use internal combustion engines. The demand for light and ignition batteries is significantly impacted by urbanization, the expansion of the automotive industry in emerging regions, and the growing appeal of electric and hybrid vehicles. Lead-acid batteries are still used in many EVs and HEVs for emergency starting and auxiliary power. One important motivator has been the development of new technologies in light and ignition batteries. Over time, these batteries have changed to satisfy the needs of contemporary automobiles and to adhere to stricter pollution regulations. Because of their increased performance, dependability, and longevity, enhanced battery designs—such as absorbent glass mat (AGM) and enhanced flooded batteries (EFB)—are appropriate for start-stop systems, which are becoming more and more prevalent in automobiles in an effort to increase fuel efficiency. Regulations pertaining to safety and vehicle emissions have a big impact on light and ignition batteries. The vehicle industry is compelled by strict emissions regulations to implement fuel-saving technologies, like start-stop systems that use sophisticated batteries. Innovations in battery design and materials are being driven by environmental considerations, such as sustainability and recycling. More efforts are being made to improve recycling procedures and reduce the environmental impact as a result of governments throughout the world enforcing stricter laws on the disposal and recycling of lead-acid batteries.
Valve Regulated Led Acid (VRLA) Batteries Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, the Valve Regulated Led Acid (VRLA) Batteries sector is anticipated to hold a dominant position throughout the projected period. VRLA Batteries are a particular kind of lead-acid battery that doesn't require electrolyte maintenance or water addition because of its sealed construction. Frequently utilized in a variety of applications, their dependability and safety earn them the nickname "maintenance-free batteries." The main characteristic of VRLA batteries is their safety valve and recombination mechanism, which regulate the gas released while charging and make them suitable for enclosed and indoor settings. Applications widely use VRLA batteries, making them a flexible market category for industrial lead-acid batteries. Telecommunications, emergency lighting, security systems, medical equipment, electric wheelchairs, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems are some examples of these uses. VRLA batteries are used in the telecom sector to supply backup power for central offices and cell towers, guaranteeing that communication services continue to function even in the event of a power loss.
The ability of VRLA batteries to offer reliable backup power solutions is one of their main selling points. Critical systems and applications that need continuous power in the event of electrical grid fluctuations or outages are ideally suited for VRLA batteries. VRLA batteries are a crucial part of UPS systems, enabling smooth backup power changes in the event of a power outage. For data centers, hospitals, and industrial facilities—where even a short power outage can have major repercussions—this is essential.
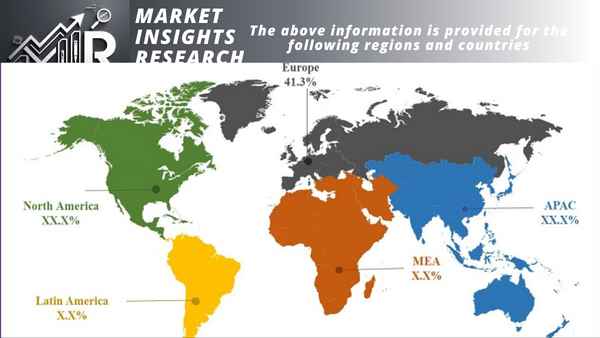
Regional Insights
With more than 40% of the industrial lead acid battery market in 2022, Asia Pacific is the largest market. The rising need for lead acid batteries in motive power, UPS, and telecommunications applications is responsible for the market's expansion in Asia Pacific. In Asia Pacific, China is the biggest market for industrial lead-acid batteries.
North AmericaWith more than 25% of the market share in 2022, North America is the second-largest market for industrial lead-acid batteries. The increasing need for lead acid batteries in telecom, UPS, and motive power applications is responsible for the market's expansion in North America. North America's biggest market for industrial lead-acid batteries is the US.
EuropeWith more than 20% of the market in 2022, Europe is the third-largest market for industrial lead-acid batteries. The increasing need for lead acid batteries in motive power, UPS, and telecommunications applications is responsible for the market's expansion in Europe. The European market for industrial lead-acid batteries is dominated by Germany.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In April 2022, East Penn Manufacturing Co., a leading manufacturer of industrial lead acid batteries, announced an investment of USD 100 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Pennsylvania, United States. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant and to upgrade the existing facilities. The expansion is expected to create over 200 new jobs.
- In May 2022, Amara Raja Batteries Ltd., a leading manufacturer of industrial lead acid batteries in India, announced an investment of USD 127 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Tamil Nadu, India. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant and to upgrade the existing facilities. The expansion is expected to create over 1,000 new jobs.
- In June 2022, EnerSys, a leading manufacturer of industrial lead acid batteries, announced an investment of USD 52 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Europe. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant in Germany. The expansion is expected to create over 100 new jobs.
- In July 2022, GS Yuasa International Ltd., a leading manufacturer of industrial lead acid batteries, announced an investment of USD 87 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Japan. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant in Japan. The expansion is expected to create over 500 new jobs.
- In August 2022, Johnson Controls International PLC, a leading manufacturer of industrial lead acid batteries, announced an investment of USD 50 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in the United States. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant in the United States. The expansion is expected to create over 100 new jobs.
Key Market Players
- EnerSys
- Stryten Energy LLC
- GS Yuasa Corporation
- East Penn Manufacturing Co. (US)
- Johnson Controls International PLC
- C&D Technologies Inc
- Crown Battery Manufacturing Co.
- Hoppecke AG
- NorthStar Battery Company
- Saft Groupe
|
By Product |
By Construction Method |
By Sales Channel |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Residential Electric Boiler Market Size - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), Industry Analysis Report, Reg...
- Europe Steam Boiler Market - By Capacity, By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), ...
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Residential Boiler Market Size By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil,...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Snapshot
-
1.2 Key Developments and Trends
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Scope and Objectives
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Classification
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What Are Industrial Lead Acid Batteries?
-
3.2 Key Applications in Backup, Motive, and Stationary Power
-
3.3 Advantages and Limitations Compared to Other Chemistries
-
3.4 Value Chain Analysis and Ecosystem Overview
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Market Drivers
-
4.1.1 Growing Demand in Material Handling and Warehousing Equipment
-
4.1.2 Cost-Effectiveness and Mature Technology
-
4.1.3 High Demand in UPS Systems and Grid Backup
-
-
4.2 Market Restraints
-
4.2.1 Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Pressure
-
4.2.2 Competition from Lithium-Ion and Advanced Batteries
-
-
4.3 Market Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Use in Telecom and Off-Grid Renewable Systems
-
4.3.2 Growth in Circular Economy and Recycling Infrastructure
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Flooded Lead Acid Batteries
-
5.2 Valve-Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) Batteries
-
5.2.1 Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM)
-
5.2.2 Gel Cells
-
-
5.3 Battery Architecture and Electrochemical Characteristics
-
5.4 Recycling and Lifecycle Management
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Product Type
-
6.1.1 Stationary Batteries
-
6.1.2 Motive Power Batteries
-
-
6.2 By Application
-
6.2.1 Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
-
6.2.2 Telecom
-
6.2.3 Forklifts and Industrial Vehicles
-
6.2.4 Power Utilities and Grid Storage
-
6.2.5 Others
-
-
6.3 By End-Use Industry
-
6.3.1 Manufacturing
-
6.3.2 Energy & Utilities
-
6.3.3 Logistics and Transportation
-
6.3.4 Commercial Infrastructure
-
-
-
Regional Analysis
-
7.1 North America
-
7.2 Europe
-
7.3 Asia-Pacific
-
7.4 Latin America
-
7.5 Middle East & Africa
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue and Volume Forecast by Region and Segment
-
8.2 Cost and Price Trends
-
8.3 Supply Chain Analysis and Import/Export Trends
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share Analysis
-
9.2 Key Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 Exide Technologies
-
9.2.2 EnerSys
-
9.2.3 East Penn Manufacturing
-
9.2.4 GS Yuasa
-
9.2.5 Amara Raja Batteries
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Strategic Developments and Industry Consolidation
-
-
Regulatory and Environmental Framework
-
10.1 Lead Handling and Disposal Regulations
-
10.2 Battery Recycling Standards and E-Waste Guidelines
-
10.3 Transport and Safety Compliance
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 Smart Monitoring and BMS in Lead Acid Systems
-
11.2 Hybrid Lead-Lithium Systems for Enhanced Performance
-
11.3 Sustainability Trends and ESG Reporting
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 References and Sources
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
