Commercial Lead Acid Battery Market
Commercial Lead Acid Battery Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, Segmented By Product (Stationary, Motive, and Start Light & Ignition Batteries (SLI)), By Construction Method (Flooded and Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) Batteries), By Sales Channel (Original Equipment Market (OEM) & Aftermarket) By Region, Competition, 2018-2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
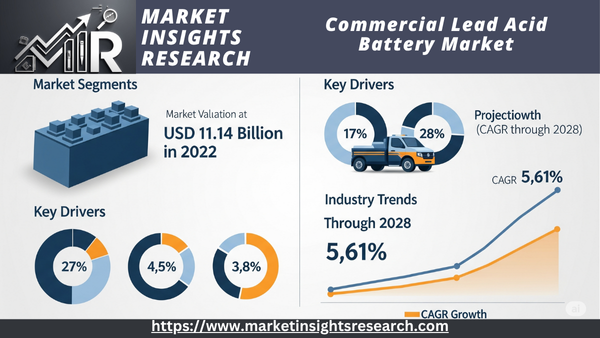
| Market Size (2022) | USD 11.14 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 5.61% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | Start Light & Ignition Batteries (SLI) |
| Largest Market | Asia-Pacific |
Market Overview
Global Commercial lead acid battery Market was valued at USD 11.14 Billion in 2022 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of 5.61% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Key Market Drivers
The growth of data centers and IT infrastructure is a key market driver.
The market for commercial lead-acid batteries is significantly influenced by the growth of IT infrastructure and the proliferation of data centers. Large volumes of digital information are processed and stored in data centers, which are vital hubs that need constant electricity to maintain data integrity and avoid expensive outages.
ReliabilityCommercial lead-acid batteries provide a dependable backup power source that smoothly steps in when grid power is interrupted. They are frequently included into uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. Maintaining continuous operations and protecting sensitive data depend on this dependability.
ScalabilityCommercial lead-acid batteries are easily scalable to supply the required backup power capacity as data centers grow and their power requirements rise. Data centers can accommodate expanding demands for energy storage thanks to this scalability.
Energy EfficiencyCommercial lead-acid batteries are well-suited for data centers where quick power changes are essential due to their reputation for being energy-efficient in short-duration, high-rate discharge applications.
Telecommunications Infrastructure Development
The need for commercial lead-acid batteries is being driven by the ongoing development of telecommunications networks and the introduction of 5G technology. To provide continuous communication services, telecommunications infrastructure—such as central offices and cell towers—needs dependable backup power.
Network ResilienceIn the event of a power outage, networks can continue to function thanks to commercial lead-acid batteries, which supply backup power for telecom equipment. Both overall network resilience and emergency communication capabilities depend on this.
Remote Site PowerCommercial lead-acid batteries are frequently used to store energy produced by solar panels or other renewable sources in isolated or off-grid areas. Telecommunications facilities can function without relying on the grid because to this energy storage.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Expansion of Healthcare Facilities
The desire for cutting-edge medical services and population increase are driving the expansion of the healthcare industry. Commercial lead-acid batteries are used in hospitals and other healthcare institutions to provide constant power for vital systems and life-saving medical equipment.
Life Support SystemsIn medical facilities, continuous electricity is necessary for operating rooms, patient monitoring devices, and life support systems. For these vital applications, commercial lead-acid batteries offer a reliable backup power source.
Regulation ComplianceStrict regulations apply to healthcare facilities, and installing backup power systems is frequently required. Healthcare providers can achieve these compliance requirements with the help of commercial lead-acid batteries, which are an affordable option.
Growth of E-commerce Warehousing
Large-scale warehouses and distribution centers have grown as a result of the rise of e-commerce. Forklifts and conveyor systems, among other materials handling equipment, are powered by commercial lead-acid batteries in these sites.
Material Handling EfficiencyBecause lead-acid batteries can produce a high current output, they are frequently utilized to power electric forklifts, enabling effective material handling activities in warehouses.
Cost-Effective SolutionCommercial lead-acid batteries are more affordable than other energy storage technologies in warehousing settings where sizable battery fleets are necessary.
Renewable Energy Integration
The need for energy storage products like commercial lead-acid batteries is being driven by the incorporation of renewable energy sources like solar and wind into commercial buildings.
system StabilizationWhen renewable energy supply is low or demand is high, commercial buildings equipped with solar arrays can employ commercial lead-acid batteries to store extra energy and inject stored electricity into the system to stabilize it.
Energy Cost ReductionBusinesses can save money on electricity costs by storing extra renewable energy, which lessens their dependency on the grid during times of high demand.
Growth in Industrial Automation
Reliable backup power is necessary to avoid expensive production disruptions caused by the growing use of industrial automation and robots in commercial and manufacturing environments.
Uninterrupted ProductionTo prevent production halts and preserve product quality, automated industrial processes must continue to run. Commercial lead-acid batteries supply essential automation systems with backup power.
Protection of Sensitive EquipmentRobotics and precision industrial machinery are frequently vulnerable to power variations. These devices are protected from damage and downtime by commercial lead-acid batteries, which guarantee clean and steady power.
In conclusion, the expansion of data centers, telecommunications infrastructure, healthcare facilities, e-commerce warehousing, integration of renewable energy, and industrial automation are the main factors propelling the commercial lead-acid battery market. These factors emphasize how important commercial lead-acid batteries are for offering dependable backup power for a variety of commercial and industrial uses.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Government Policies are Likely to Propel the Market
Environmental Regulations and Recycling Mandates
The market for commercial lead-acid batteries is significantly impacted by government regulations pertaining to battery recycling and environmental protection. These regulations are intended to guarantee the appropriate recycling and disposal of lead-acid batteries, reduce their negative effects on the environment, and encourage environmentally friendly business activities.
Recycling RequirementsA number of nations mandate that producers of lead-acid batteries set up and finance recycling initiatives. With an emphasis on recovering valuable elements like lead and plastic, these initiatives make sure that spent batteries are gathered, transported, and recycled in an environmentally friendly manner.
Pollution ControlGovernments enforce stringent emissions regulations on lead-acid battery manufacturing sites in order to safeguard the purity of the air and water. By minimizing the emissions of sulfuric acid and lead into the environment, these safeguards lower the danger of pollution.
Battery Labeling and DisposalClear labeling and instructions for the safe handling and disposal of lead-acid batteries are frequently required by regulations. To avoid contaminating the environment, this includes guidelines for recycling and proper disposal techniques.
Energy Storage Incentives and Grants
To encourage the use of energy storage technologies, such as commercial lead-acid batteries, across a range of industries, numerous governments provide grants, funding programs, and incentives. Grid stability and sustainable energy technologies are the goals of these strategies.
Energy Storage Tax CreditsCompanies and industries that invest in energy storage products, such as commercial lead-acid batteries, may be eligible for tax credits from the government. These tax breaks lower the initial cost of battery installations, increasing their viability from an economic standpoint.
Research and Development GrantsGovernment organizations frequently provide funds for energy storage technology research and development initiatives. These grants promote creativity and the creation of commercial lead-acid batteries that are more economical and efficient.
Grid Integration Standards
Establishing guidelines and standards for the smooth integration of energy storage devices, such as commercial lead-acid batteries, into the electrical grid is a crucial responsibility of governments.
Grid Compatibility StandardsTo guarantee that energy storage devices can safely and successfully support grid operations, regulations may establish particular standards and requirements. Commercial lead-acid batteries must adhere to these requirements in order to operate dependably in grid-connected applications.
Demand Response ProgramsTo lessen peak demand on the grid, governments may put in place demand response programs that incentivize companies and industries to adopt energy storage. Participants may be eligible for incentives or discounted electricity rates.
Industrial and Commercial Energy Efficiency Standards
Adoption of energy storage technologies, such as commercial lead-acid batteries, is indirectly influenced by government programs intended to increase energy efficiency in the commercial and industrial sectors.
Minimum Efficiency StandardsMinimum energy efficiency requirements for commercial and industrial systems and equipment may be set by regulations. Businesses looking to cut expenses and energy use are more likely to use energy storage options that satisfy these requirements.
Energy Performance CertificationsTo encourage companies to invest in energy-efficient technology like energy storage, governments may mandate that commercial buildings receive energy performance certifications.
Investment in Critical Infrastructure
Government initiatives that place a high priority on funding vital infrastructure, such emergency services, communication, and transportation, increase demand for dependable backup power sources, such as commercial lead-acid batteries.
Funding for Emergency ServicesGovernments set aside money for emergency services, such as police stations, fire departments, and hospitals. During grid outages, many facilities depend on backup power to continue critical operations.
Governments may need backup power systems in charging infrastructure as they encourage the electrification of public transportation, which presents prospects for the installation of commercial lead-acid batteries.
Renewable Energy Integration Targets
The use of commercial lead-acid batteries as part of energy storage systems for renewable energy projects is fueled by government policies that establish targets and incentives for the integration of renewable energy.
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS)RPS are frequently set by governments and require a specific proportion of power to be generated from renewable sources. Commercial lead-acid batteries and other energy storage technologies are needed by renewable energy projects in order to accomplish these goals by storing excess energy and maintaining system stability.
Feed-In Tariffs (FiTs)Businesses and industries who feed excess renewable energy back into the grid may be compensated by the implementation of FiTs. By strategically storing and releasing energy, energy storage systems—such as commercial lead-acid batteries—allow enterprises to optimize their benefits under FiT programs.
In summary, government policies and regulations have a big impact on the market for commercial lead-acid batteries because they affect recycling habits, offer financial incentives, establish grid integration standards, encourage energy efficiency, support vital infrastructure, and encourage the use of renewable energy sources. These regulations are essential in determining how commercial lead-acid batteries are used in industry and commerce in a sustainable and effective way.
Key Market Challenges
Environmental Concerns and Recycling
Environmental issues and recycling present a significant problem for the commercial lead-acid battery sector. Despite their widespread use and dependability, lead-acid batteries are dangerous for the environment since they contain lead, sulfuric acid, and other dangerous substances. For the industry to remain sustainable, these issues must be resolved.
Lead Pollution and RecyclingLead is a hazardous heavy metal that, if improperly handled, can present serious health and environmental hazards. Lead-acid batteries remain a source of lead pollution despite massive recycling efforts, particularly in areas with weak recycling infrastructure or loose legislation. As a result, ecosystems and human health may be impacted by contaminated soil and water.
Regulatory ComplianceTo reduce environmental hazards, governments enforce stringent laws governing the production, recycling, and disposal of lead-acid batteries. Manufacturers must make investments in environmentally friendly production methods and effective recycling facilities in order to comply with these rules, which raises operating expenses.
Infrastructure for Battery RecyclingThe availability of recycling infrastructure and consumer involvement are critical to the success of lead-acid battery recycling. The collecting, transportation, and recycling of spent batteries present difficulties, particularly in areas with a dearth of recycling infrastructure.
Transition to Cleaner TechnologiesA move toward cleaner and more sustainable energy storage technologies is being fueled by environmental concerns surrounding lead-acid batteries. The ongoing viability of lead-acid batteries in a market that is changing quickly is threatened by this shift.
Technological Advancements and Competition
Emerging energy storage technologies, especially lithium-ion batteries and upgraded lead-acid battery types, are a threat to the commercial lead-acid battery market. Traditional lead-acid batteries face a serious threat from technological developments in these alternative technologies.
Competition from Lithium-Ion BatteriesCompared to conventional lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries have benefits such a higher energy density, a longer cycle life, and quicker charging. Because of these characteristics, lithium-ion batteries are becoming more and more appealing for commercial use, particularly in sectors that demand high power density and quick cycling.
Advanced Lead-Acid TechnologiesTo compete with lithium-ion batteries and increase performance, lead-acid battery innovations like Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) and Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB) are being developed. These developments might not, however, always be comparable to the better qualities of lithium-ion batteries.
Energy Density and Space RestrictionsLithium-ion batteries with comparable energy storage capacity are lighter and more compact than conventional lead-acid batteries. This restricts its applicability in settings with limited space, such data centers or electric cars.
Sustainability IssuesNew energy storage technologies frequently portray themselves as greener alternatives to lead-acid batteries, which could influence business purchasers looking for sustainable solutions.
Costs of Research and DevelopmentLead-acid battery producers must spend money on research and development to improve performance, prolong cycle life, and satisfy changing industry standards if they want to stay competitive. These expenditures have an effect on pricing and can be significant.
In summary, the market for commercial lead-acid batteries faces difficulties with recycling, environmental issues, competition from other technologies, and the requirement for constant technological development. The industry must address these issues by implementing cleaner manufacturing procedures, boosting battery performance, improving recycling procedures, and investigating new markets and uses if it hopes to be relevant and sustainable.
Segmental Insights
Start Light & Ignition Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, the Start Light & Ignition category is anticipated to hold a dominant position throughout the projected period. The main purpose of light and ignition batteries is to supply the initial power boost needed to start internal combustion engine-powered vehicles, such as trucks, buses, commercial vehicles, and industrial machinery. They play a crucial part in making sure commercial fleets start up consistently, particularly in sectors like transportation and logistics. Light and ignition batteries are essential to the day-to-day functioning of fleets of commercial vehicles in commercial environments. For delivery trucks, buses, and other commercial vehicles to start dependably and adhere to strict timetables, these batteries are necessary. Light and ignition batteries' dependability is essential in sectors where supply chain interruptions and large financial losses can arise from vehicle outages. Light and ignition batteries are distinguished by their capacity to provide a large amount of cranking power in a brief period of time, which enables them to efficiently start commercial vehicles' engines even in inclement weather. Extreme temperatures and uneven terrain are just two of the many settings in which commercial trucks frequently operate. Commercial fleets are guaranteed to operate consistently since Light & Ignition Batteries are made to function dependably in these circumstances. Seasonal changes, such frigid winters, can have a big effect on how well Light & Ignition Batteries work in business settings. Vehicle starting might be more difficult in colder climates because of decreased battery efficiency. To guarantee dependable vehicle starting throughout the winter, many commercial fleet operators make investments in Light & Ignition Batteries with high cold-cranking amps (CCA) ratings.
For the administration of commercial fleets, it is essential to make sure that light and ignition batteries are properly maintained and replaced. To prevent unforeseen problems with vehicle starting, fleet operators regularly check battery voltage, test loads, and replace old batteries. For business fleets, changing batteries is a routine maintenance procedure. This proactive approach helps to avoid operational problems.
Valve Regulated Led Acid (VRLA) Batteries Insights
With the biggest market share in 2022, the Valve Regulated Led Acid (VRLA) Batteries sector is anticipated to hold a dominant position throughout the projected period. Because of their adaptability, VRLA Batteries are often used in commercial settings. They are used in a variety of ways to help businesses and industries with their energy storage and backup power demands. Backup power solutions are one of the main uses for VRLA Batteries in commercial settings. These batteries are essential to businesses and industries because they guarantee the ongoing operation of vital systems and equipment by supplying power during electrical grid outages. Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, which automatically transition to battery power in the event of a grid power outage, frequently incorporate VRLA Batteries. This type of battery is essential for protecting industrial processes, data centers, and delicate electronics. VRLA Batteries are essential for storing extra energy produced by renewable energy sources like solar and wind, which are becoming more and more common in commercial buildings and facilities. When energy generation is high, businesses can store excess energy to utilize during peak demand or when renewable energy production is low. By enabling businesses to minimize their dependency on the grid, cut their electricity costs, and maximize the usage of clean, renewable energy, VRLA Batteries promote energy independence. Businesses and industries depend on the dependable operation of telecommunications networks, which include central offices and cell towers. VRLA Batteries provide backup power to ensure continuous communication services in the event of a power loss caused by a natural disaster or other disturbance. This is necessary to enable business continuity, preserve emergency communication capabilities, and guarantee that critical communications continue to function.
Regional Insights
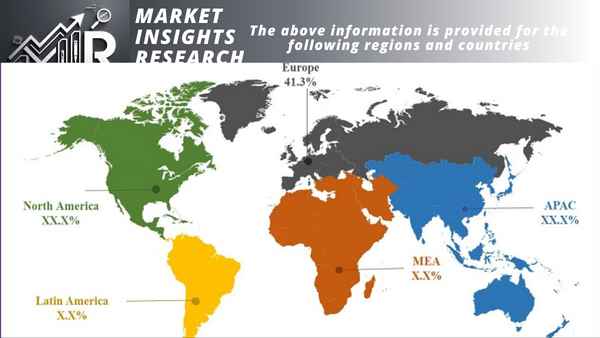
With more than 40% of the market in 2022, Asia Pacific is the biggest market for commercial lead acid batteries. The rising demand for lead acid batteries in China and India is responsible for the market's expansion in the Asia Pacific region. Asia Pacific's two biggest markets for commercial lead acid batteries are China and India.
With more than 25% of the market in 2022, North America is the second-largest market for commercial lead acid batteries. The rising demand for lead acid batteries in the US and Canada is responsible for the market's expansion in North America. North America's biggest market for commercial lead acid batteries is the US.
With more than 20% of the market in 2022, Europe is the third-largest market for commercial lead acid batteries. The rising demand for lead acid batteries in Germany, France, and the UK is responsible for the market's expansion in Europe. The European market for commercial lead acid batteries is dominated by Germany.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In January 2022, EnerSys, a leading manufacturer of lead acid batteries, announced an investment of USD 100 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in the United States. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant in Pennsylvania, United States. The expansion is expected to create over 200 new jobs.
- In February 2022, GS Yuasa International Ltd., a leading manufacturer of lead acid batteries in Japan, announced an investment of USD 87 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Japan. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant in Japan. The expansion is expected to create over 500 new jobs.
- In March 2022, Johnson Controls International PLC, a leading manufacturer of lead acid batteries in the world, announced an investment of USD 52 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Europe. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant in Germany. The expansion is expected to create over 100 new jobs.
- In April 2022, East Penn Manufacturing Co., a leading manufacturer of lead acid batteries in the United States, announced an investment of USD 100 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Pennsylvania, United States. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant and to upgrade the existing facilities. The expansion is expected to create over 200 new jobs.
- In May 2022, Amara Raja Batteries Ltd., a leading manufacturer of lead acid batteries in India, announced an investment of USD 127 million to expand its manufacturing capacity in Tamil Nadu, India. The investment will be used to build a new manufacturing plant and to upgrade the existing facilities. The expansion is expected to create over 1,000 new jobs.
Key Market Players
- EnerSys
- Stryten Energy LLC
- GS Yuasa Corporation
- East Penn Manufacturing Co. (US)
- Johnson Controls International PLC
- C&D Technologies Inc
- Crown Battery Manufacturing Co.
- Hoppecke AG
- NorthStar Battery Company
- Saft Groupe
|
By Product |
By Construction Method |
By Sales Channel |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Gas Fired Boiler Market Size - By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 - 100 MMBtu/hr, > 100 - 250 MMBtu/...
- Europe Residential Boiler Market Size - By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural ...
- U.S. Boiler Market Size By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), Capacity, By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), By Produ...
- Commercial Hot Water Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Con...
- UK Commercial Boiler Market Size By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity, By Technology (Condensing, Non...
- Residential Electric Boiler Market Size - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), Industry Analysis Report, Reg...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Snapshot
-
1.2 Key Insights and Forecast Trends
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Objectives and Scope
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Classification
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What Are Commercial Lead Acid Batteries?
-
3.2 Market Evolution and Technology Lifecycle
-
3.3 Comparison with Other Battery Chemistries (Li-ion, NiMH)
-
3.4 Value Chain and Key Stakeholders
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Drivers
-
4.1.1 Established Use in Backup Power and Telecom
-
4.1.2 Cost-Effectiveness and Recycling Capability
-
4.1.3 High Adoption in HVAC, Retail, and Commercial Lighting Systems
-
-
4.2 Restraints
-
4.2.1 Environmental Risks and Disposal Costs
-
4.2.2 Rise of Competitive Lithium Technologies
-
-
4.3 Opportunities
-
4.3.1 Expansion in E-commerce Warehouses and Data Centers
-
4.3.2 Demand in Solar-Integrated Commercial Backup Systems
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Flooded Lead Acid Batteries
-
5.2 Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) Batteries:
-
5.2.1 AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat)
-
5.2.2 Gel Batteries
-
-
5.3 Battery Construction and Electrochemistry
-
5.4 Lifecycle, Maintenance, and Efficiency Metrics
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Product Type
-
6.1.1 Stationary
-
6.1.2 Motive Power
-
-
6.2 By Application
-
6.2.1 Commercial Buildings and Offices
-
6.2.2 Data Centers and IT Infrastructure
-
6.2.3 Retail Stores and Malls
-
6.2.4 Telecom Base Stations
-
6.2.5 Emergency Lighting Systems
-
6.2.6 Others
-
-
6.3 By Voltage Rating
-
6.3.1 Below 12V
-
6.3.2 12V–48V
-
6.3.3 Above 48V
-
-
-
Regional Market Analysis
-
7.1 North America
-
7.2 Europe
-
7.3 Asia-Pacific
-
7.4 Latin America
-
7.5 Middle East & Africa
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue and Volume Forecast
-
8.2 Segment-Wise Demand Outlook
-
8.3 Pricing Trends and Recycling Economics
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share and Competitive Mapping
-
9.2 Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 EnerSys
-
9.2.2 Exide Technologies
-
9.2.3 Amara Raja Batteries
-
9.2.4 East Penn Manufacturing
-
9.2.5 GS Yuasa
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Strategic Partnerships, Product Launches, and M&A
-
-
Regulatory and Sustainability Framework
-
10.1 Battery Safety, Handling, and Transport Standards
-
10.2 Environmental Regulations for Commercial Battery Disposal
-
10.3 Circular Economy and Recycling Compliance
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 Smart Monitoring and BMS Integration
-
11.2 Hybridization and Advanced Grid Services
-
11.3 Role in Green Commercial Infrastructure
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 References and Sources
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
