Smart Gas Meter Market
Smart Gas Meter Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast Segmented By Component (AMR and AMI), By Type (Smart Ultrasonic Gas Meter and Smart Diaphragm Gas Meter), By Component (Hardware and Software), By End User (Residential, Commercial and Industrial), By Region, and By Competition 2018-2028 2018-2028
Published Date: May - 2025 | Publisher: MIR | No of Pages: 320 | Industry: Power | Format: Report available in PDF / Excel Format
View Details Buy Now 2890 Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
| Market Size (2022) | USD 1.62 billion |
| CAGR (2023-2028) | 3.79% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | AMI |
| Largest Market | Europe |
Market Overview
The global smart gas meter market is valued at USD 1.62 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period, with a CAGR of 3.79% through 2028.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Key Market Drivers
Increasing Emphasis on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
The increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency is propelling the global smart gas meter market. There is a greater awareness of the need to minimize carbon emissions and maximize resource use as the globe struggles with climate change and environmental deterioration. Because they provide real-time data on gas consumption, smart gas meters are essential to this paradigm change because they empower utilities and consumers to make educated decisions about energy use.
Advanced functions like automatic meter reading, data analytics, and remote monitoring are available with smart gas meters. These features enable utility providers and customers to spot inefficiencies, spot trends in energy use, and put specific waste reduction plans into action. This focus on energy efficiency is in line with international programs and laws meant to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As part of larger initiatives to meet sustainability goals, governments and regulatory agencies worldwide are progressively offering incentives for the adoption of smart metering systems.
Additionally, a more responsive and intelligent energy distribution system is made possible by the integration of smart gas meters into smart grids. Better load control, faster leak or anomaly detection, and increased overall gas supply chain efficiency are all made possible by this interconnection. As a result, it is anticipated that the demand for smart gas meters would increase dramatically due to the general push for a more sustainable and greener future.
Technological Advancements and IoT Integration
The ongoing advancement of technology and the incorporation of Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities into metering systems are major factors propelling the global smart gas meter market. The continuous digital revolution has made it possible to create advanced smart gas meters that do more than just measure things. With the use of sensors, communication modules, and data processing skills, modern smart gas meters can easily gather and send data in real time.
Smart gas meters can interact with other devices through the integration of IoT technology, creating a vast and interconnected network. The development of smart cities and smart households, where energy management is more automated and intelligent, is made possible by this connectedness. Through intuitive interfaces, consumers may obtain comprehensive information on their gas usage, raising awareness and promoting energy-saving behaviors.
Additionally, smart gas meters' remote communication capabilities eliminate the need for manual meter reading, which benefits utility companies' operating efficiency. In addition to saving time and money, automated meter reading reduces the inaccuracies that come with manual data collecting. With the advent of 5G networks and edge computing, smart gas meters' capabilities are anticipated to grow even more as technology develops, propelling the global adoption of these cutting-edge metering solutions.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Regulatory Initiatives and Mandates
Mandates and regulatory actions are important factors driving the global market for smart gas meters. Globally, governments and regulatory agencies are realizing more and more how smart metering technology may improve overall utility operations, lower carbon emissions, and increase energy efficiency. Because of this, numerous nations are putting in place legal frameworks that either encourage or require the installation of smart gas meters.
Smart gas meters are seen to be essential to achieving strict goals for lowering carbon footprints and increasing energy efficiency in a number of areas. Utilities are frequently required by regulatory obligations to switch from conventional gas meters to smart ones within a given time limit. In addition to encouraging the use of smart gas meters, these programs foster an atmosphere that is favorable to investment and innovation in the smart metering industry.
Furthermore, financial incentives and subsidies for utilities and consumers adopting smart gas metering solutions are examples of regulatory support that goes beyond deployment regulations. These incentives speed up the switch to more sophisticated and environmentally friendly metering infrastructure by assisting in the removal of financial obstacles. The desire for regulatory compliance and the pursuit of energy efficiency goals are expected to propel the global smart gas meter market's steady rise as regulatory frameworks continue to change and become more receptive to smart metering technology.
Key Market Challenges
High Initial Implementation Costs and Return on Investment Concerns
The high upfront implementation costs of smart metering infrastructure deployment are a major obstacle for the global smart gas meter market. In addition to the cost of the meters themselves, switching from conventional to smart gas meters also entails costs for installation, data management systems, and connectivity infrastructure. Although smart gas meters provide clear long-term advantages including increased efficiency and lower operating costs, the initial capital outlay may be prohibitive for end customers as well as utility corporations.
The difficulty for utility companies is in defending the large upfront investment to regulators and stakeholders. Showing the technology's long-term worth and operational benefits is crucial because smart gas meters' return on investment (ROI) is usually realized over a long period of time. Furthermore, customers can be reluctant to pay for the installation of smart meters, particularly if the advantages are not immediately noticeable. One of the biggest obstacles to the broad deployment of smart gas meters is persuading stakeholders and customers of the technology's long-term benefits and financial feasibility.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Significant worries about data security and privacy are raised by the widespread use of connected devices and the vast data collection possibilities of smart gas meters. Sensitive usage data is continuously collected and transmitted by smart gas meters, giving users important insights into their daily routines and activities. Therefore, safeguarding this data against cyber threats, illegal access, and possible misuse becomes a top priority for the global smart gas meter market.
Strong cybersecurity measures must be put in place by utility companies and technology providers to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the data produced by smart gas meters. Customers' privacy concerns are heightened by the possibility of illegal access to consumption patterns, which makes them skeptical and resistant to the use of smart metering systems. Transparent communication of the safeguards in place to protect consumer data and adherence to strict data protection laws are necessary to allay these worries.

Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Regulatory and Standards Hurdles
For industry participants, navigating intricate regulatory environments and attaining standardization in the global smart gas meter market is a major task. Regional differences in the laws governing the installation of smart gas meters have resulted in a fragmented industry with a range of requirements and compliance criteria. Different regulatory frameworks that utility companies operating in many jurisdictions must deal with can make it difficult for smart metering technologies to integrate and scale seamlessly.
Furthermore, interoperability and compatibility issues arise due to the lack of uniform standards for smart gas meters. Integrating disparate devices into a coherent system can be challenging since different manufacturers may create meters with different data formats and connection protocols. In order to establish an open and interoperable environment and facilitate smooth communication between smart gas meters and other smart grid components, a standardized approach is essential.
Industry participants, such as government agencies, utility companies, and IT companies, must work together to create common frameworks and standards in order to address these issues. Overcoming obstacles pertaining to compliance and interoperability will help create a more unified and globally connected smart gas meter market by streamlining regulatory procedures and encouraging international collaboration.
Key Market Trends
Integration with Advanced Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
The combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and sophisticated analytics is a new trend in the global smart gas meter market that aims to increase operational efficiency and decision-making power. Large volumes of data about equipment performance, system status, and gas consumption trends are produced by smart gas meters. Utility firms can gain important insights from this data by utilizing AI and advanced analytics, which makes it possible to forecast demand, optimize gas distribution networks, and do predictive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance is a crucial use case for advanced analytics, where AI systems examine data from smart gas meters to anticipate problems or equipment breakdowns before they arise. This proactive strategy improves overall system reliability, prolongs equipment lifespan, and decreases downtime. Furthermore, utility firms may optimize resource allocation and guarantee a consistent and dependable gas supply for customers by anticipating peak usage periods with the aid of demand forecasting driven by advanced analytics.
Additionally, analytics powered by AI aid in the creation of services that are more focused on the needs of the client. Utility providers can promote a more efficient use of resources by customizing pricing plans and energy-saving recommendations for individual customers based on their understanding of usage patterns and preferences. By combining these technologies, gas distribution is becoming more intelligent and data-driven, which puts the global smart gas meter market at the front of the energy industry's larger digital revolution.
Expansion of Smart Gas Metering in Developing Economies
The growing use and spread of smart gas metering in developing nations is a noteworthy trend in the global smart gas meter market. The benefits of smart meters are increasingly being recognized in emerging economies, despite the fact that their initial implementation was concentrated in developed regions. Smart gas meter adoption is being driven by the growing need for sustainable and effective energy management solutions as these countries become more urbanized and industrialized.
Traditional gas metering infrastructure may be antiquated or ineffective in many developing nations, which can result in problems including incorrect billing and challenges with managing and monitoring gas delivery. By offering real-time data, remote monitoring capabilities, and increased meter reading accuracy, smart gas meters provide an answer to these problems. Smart gas meter deployment in developing nations is consistent with larger initiatives to improve energy efficiency and update utility infrastructure.
Additionally, international partnerships, regulatory frameworks, and government initiatives frequently encourage the growth of smart gas metering in developing economies. Governments are aware of how smart metering technology can help with energy-related issues, lower gas distribution losses, and improve the resilience of infrastructure as a whole. Because of this, utility firms in these areas are spending more money on smart gas metering systems, which is helping the industry expand globally. This trend shows that smart gas meters are becoming more widely used and inclusive, opening up modern metering technologies to a wider range of people worldwide.
Segmental Insights
Type
In 2022, the market leader was the Smart Ultrasonic Gas Meter category. This cutting-edge metering system has various benefits over conventional mechanical meters since it measures gas flow using ultrasonic sensors. The excellent precision and accuracy of smart ultrasonic gas meters in measuring gas flow is well-known. In contrast to mechanical meters, which could deteriorate with time, ultrasonic technology guarantees accurate and constant readings. A major factor in the uptake of smart ultrasonic gas meters is their capacity to deliver precise data on gas consumption, particularly in situations where exact measurement is essential.
Smart Ultrasonic Gas Meters' lifetime and endurance are influenced by the non-intrusive nature of ultrasonic measurements. Because these meters don't have any moving parts that could break, they require less maintenance, which lowers electricity companies' operating expenses. Smart Ultrasonic Gas Meters are a desirable investment for end users and utility companies alike due to their extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs.
The incorporation of modern communication technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) is a noteworthy trend in the Smart Ultrasonic Gas Meter market. By facilitating smooth communication between meters and central systems, this integration improves connection. Efficient real-time data transmission is a key component in the creation of smart cities and smart grids.
Component
We anticipate a rapid increase in the hardware category over the forecast period. The actual tools and parts that make it possible to measure, communicate, and control gas usage are included in the hardware segment, which is a significant part of the global smart gas meter market.
One of the main forces behind innovation in the smart gas meter hardware market is the ongoing advancement of technology. More precise, dependable, and effective hardware solutions are developed as a result of developments in sensor technologies, communication modules, and meter building materials. Hardware components are becoming increasingly complex as technology develops, allowing for increased performance and better functionality.
The adoption of smart gas meters is largely driven by regulatory initiatives and regulations, which also have an impact on the features and specifications of hardware components. Smart meter implementation is being promoted by governments and regulatory agencies worldwide to meet sustainability and energy efficiency targets. Innovation in the hardware sector is fueled by the requirement to integrate particular hardware characteristics, such as data encryption and communication protocols, to comply with regulatory mandates.
Designing hardware components with lifespan and durability in mind is becoming more and more popular. We anticipate that smart gas meters will endure for an extended period with minimal maintenance. Creating hardware that can handle different conditions and last a long time is made easier by using parts that resist environmental factors and choosing strong materials.
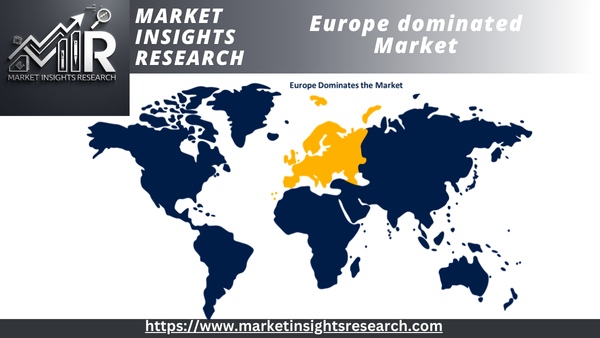
Regional Insights
With the most market share in 2022, Europe became the dominant region. Europe has led the way in enforcing laws and regulations meant to modernize utility systems and encourage energy efficiency. Directives from the EU, such the Clean Energy for All Europeans package, establish aggressive goals to increase the proportion of renewable energy sources and lower greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations fuel the extensive use of smart gas meters as part of an all-encompassing plan to meet environmental objectives.
Reducing carbon footprints and increasing energy efficiency are priorities for European nations. Smart gas meters are essential in this situation because they provide real-time data on gas consumption, allowing utility providers and consumers to optimize energy use. Europe's commitment to creating a more sustainable and energy-efficient future is in line with the capacity to effectively monitor and control gas usage.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is being widely deployed throughout Europe, integrating smart gas meters into all-encompassing smart grid systems. AMI makes it possible for meters and central systems to communicate in both directions, allowing for remote monitoring and real-time data sharing. This pattern is in line with Europe's goal of creating energy networks that are more robust and effective.
In Europe, integrating renewable energy sources into the grid is a noteworthy trend. Smart gas meters contribute to this trend by offering information that facilitates improved control and integration of renewable gas sources. Monitoring and managing the usage of renewable gases helps the area move toward a more varied and sustainable energy mix.
In summary, Europe's contribution to the global smart gas meter market is distinguished by its dedication to technological innovation, emphasis on energy efficiency, and regulatory assistance. Ongoing trends including the implementation of AMI and the incorporation of renewable energy sources, suggest a healthy trajectory for the region's smart gas metering market's continued expansion, despite ongoing issues with data privacy and cost implications.
Download Free Sample Ask for Discount Request Customization
Recent Developments
- In July 2022, Itron Inc. announced that they are collaborating with Sevier County Utility District (SCUD) to deploy Itron’s AMI Essentials for Gas, including 15,000 Itron Cellular 500G Gas Modules and Temetra, Itron’s next-generation meter data collection and management solution. The utility will be able to speed up meter readings, improve operations throughout the SCUD gas district in Tennessee, and gain greater visibility into its gas distribution system thanks to the solution. Throughout the following two years, USS will help SCUD distribute the gas modules all over its region.
- In July 2022, Italian gas distribution operator Italgas announced the introduction of Smart leak detection by launching Picarro for methane emission detection and reduction in its networks. Picarro will offer approximately 0.8 leaks/km detection rate compared to the 0.03 leaks/km of traditional gas detection.
Key Market Players
- Landis + GYR Group AG
- Wasion Group Holdings
- Elster Group GmbH
- Itron Inc.
- Azbil Kimmon Co. Ltd
- Sagemcom SAS
- Diehl Stiftung GmbH & Co. KG
- Holley Technology Ltd
- Apator SA
- Yazaki Corporation Source
|
By Technology |
By Type |
By Component |
By End User |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
Related Reports
- Europe Steam Boiler Market - By Capacity, By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal), By Technology (Condensing, Non-Condensing), ...
- Electric Boiler Market Size By Voltage Rating (Low, Medium), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Food P...
- Europe Boiler Market By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Boiler Market Size - By Fuel (Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Electric), By Capacity (≤ 10 MMBtu/hr, > 10 - 50 MMBtu/hr, > 50 ...
- Residential Boiler Market Size By Technology (Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil, Electric}, Non-Condensing {Natural Gas, Oil,...
- Commercial Electric Boiler Market - By Voltage Rating (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage), By Capacity, By Product (Hot Water,...
Table of Content
-
Executive Summary
-
1.1 Market Overview
-
1.2 Key Trends and Highlights
-
1.3 Strategic Recommendations
-
-
Introduction
-
2.1 Report Scope and Objectives
-
2.2 Research Methodology
-
2.3 Definitions and Market Classification
-
-
Market Overview
-
3.1 What Are Smart Gas Meters?
-
3.2 Evolution from Traditional to Smart Metering
-
3.3 Benefits for Utilities, Regulators, and End Users
-
3.4 Market Adoption Lifecycle and Deployment Models
-
-
Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Drivers
-
4.1.1 Growing Need for Real-Time Consumption Monitoring
-
4.1.2 Government Mandates and Smart Infrastructure Initiatives
-
4.1.3 Integration with IoT and Smart Home Ecosystems
-
-
4.2 Restraints
-
4.2.1 High Initial Setup and Maintenance Costs
-
4.2.2 Data Privacy and Security Concerns
-
-
4.3 Opportunities
-
4.3.1 AI and Predictive Analytics in Gas Demand Management
-
4.3.2 Rollouts in Emerging Urban Markets
-
-
4.4 Challenges
-
4.5 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Technology Landscape
-
5.1 Communication Technologies (RF, GSM, LoRaWAN, NB-IoT)
-
5.2 Meter Types: Diaphragm, Ultrasonic, Thermal
-
5.3 Cloud Platforms and AMI Integration
-
5.4 Data Analytics, Security Layers, and Edge Computing
-
5.5 Smart Grid and Multi-Utility Meter Compatibility
-
-
Market Segmentation
-
6.1 By Technology
-
6.1.1 Automated Meter Reading (AMR)
-
6.1.2 Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
-
-
6.2 By Component
-
6.2.1 Hardware (Meters, Modules)
-
6.2.2 Software (Billing, Analytics)
-
6.2.3 Services (Installation, Maintenance)
-
-
6.3 By End-User
-
6.3.1 Residential
-
6.3.2 Commercial
-
6.3.3 Industrial
-
-
-
Regional Analysis
-
7.1 North America
-
7.2 Europe
-
7.3 Asia-Pacific
-
7.4 Latin America
-
7.5 Middle East & Africa
-
-
Market Size and Forecast (2020–2030)
-
8.1 Revenue and Volume Projections
-
8.2 Regional and Segment-Wise Growth Analysis
-
8.3 Rollout Timelines and Adoption Benchmarks
-
-
Competitive Landscape
-
9.1 Market Share Analysis
-
9.2 Key Company Profiles
-
9.2.1 Itron Inc.
-
9.2.2 Sensus (Xylem Inc.)
-
9.2.3 Landis+Gyr
-
9.2.4 Apator Group
-
9.2.5 Aclara Technologies
-
9.2.6 Others
-
-
9.3 Strategic Alliances, Product Launches, and Innovation Pipelines
-
-
Regulatory and Policy Framework
-
10.1 Government Smart Metering Mandates
-
10.2 Safety, Calibration, and Data Handling Regulations
-
10.3 Interoperability Standards and EU/US Guidelines
-
-
Innovation and Future Outlook
-
11.1 AI-Driven Consumption Forecasting and Leak Detection
-
11.2 Interfacing with Smart Cities and ESG Reporting
-
11.3 Blockchain for Secure Gas Billing and Transactions
-
-
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
-
Appendices
-
13.1 Glossary
-
13.2 Research Methodology
-
13.3 Data Sources and References
-
To get a detailed Table of content/ Table of Figures/ Methodology Please contact our sales person at ( chris@marketinsightsresearch.com )
FAQ'S
For a single, multi and corporate client license, the report will be available in PDF format. Sample report would be given you in excel format. For more questions please contact:
Within 24 to 48 hrs.
You can contact Sales team (sales@marketinsightsresearch.com) and they will direct you on email
You can order a report by selecting payment methods, which is bank wire or online payment through any Debit/Credit card, Razor pay or PayPal.
Discounts are available.
Hard Copy
